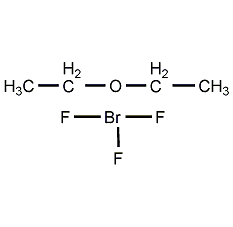
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H10BF3O |
| Molecular weight | 141.93 |
| label |
Boron trifluoride diethyl ether complex, Boron trifluoride ether, Boron trifluoride etherate, Boron fluoride ether, Boron trifluoride ethyl etherate, catalyst, Auxiliary |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-63-7
MDL number:MFCD00013194
EINECS number:203-689-8
RTECS number:None
BRN number:3909607
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless-light yellow transparent liquid with pungent odor
2. Melting point (℃): -60
3. Boiling point (℃/1.3kPa ): 124
4. Vapor pressure (kPa /20℃): 0.5
5. Vapor density: 4.9
6. Density: 1.13
7. Autoignition temperature (℃): 185
8. Lower explosion limit: 1.9%
9. Upper explosion limit: 36%
10. Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, ether and other organic solvents
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: LCLo: 50ppmmg/4H for guinea pigs. This product is toxic. Contact with eyes and skin can cause burns. Inhalation can cause high levels of poisoning. This product has irritating, corrosive and anesthetic effects on the human body.
Ecological data
Slightly hazardous to water, avoid contact of undiluted or large quantities of product with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 31.41
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 104.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 255.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.45
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 19.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
1. Sensitive to water. Avoid contact with incompatible materials, sources of fire, moist air, and water.
Reacts with water, metals, strong oxidants, acids, alkalis, alkali metals, and steel. Easily decomposes in moist air. Flammable. poisonous. Corrosive. If stored for too long, the color will become darker. Easily decomposes when exposed to moist air. 2.Highly toxic. Hydrogen fluoride gas used in production��It is 20 times more harmful to the human body than sulfur dioxide. Hydrogen fluoride mainly damages bones and can easily lead to spontaneous fractures. The human body often causes convulsions and spasms due to calcium deficiency. In severe cases, it can cause breathing difficulties, paralysis and death; secondly, it damages the skin, causing itching, dermatitis, eczema, etc. The maximum allowable concentration of hydrogen fluoride in the air is 1 mg/m3. Production equipment should be sealed to prevent running, emitting, dripping, leaking and other phenomena. Good ventilation should be maintained at the production site, and operators should wear protective equipment.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry warehouse. Keep away from heat sources and fire, no leakage, and prevent moisture.
Store in a cool, ventilated, dry place, away from fire, heat sources and combustibles, and away from water. The packaging must be labeled “corrosive and flammable liquids”. Air and railway transportation is limited.
2. Packed in plastic barrels and wooden boxes, or in sealed stainless steel cans. Store in a cool, dry, dark place. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. React the boron trifluoride gas produced by the co-heating of sulfuric acid, calcium fluoride (fluorite powder) and boric acid with diethyl ether, and the crude boron trifluoride-diethyl ether product obtained is refined into the finished product. Raw material consumption quota: boric acid (≥98%) 560kg/t, calcium fluoride (≥90%) 1150kg/t, fuming sulfuric acid (104.5%) 4100kg/t, ether (≥99%) 725kg/t.

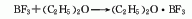
2. Absorption method
Combine boric acid with fuming Sulfuric acid and fluorite powder are heated together for reaction to generate boron trifluoride gas, which is then absorbed with diethyl ether and rectified under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product of boron trifluoride diethyl ether complex. The reaction equation is as follows:
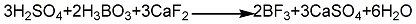
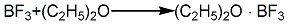
3. In addition to potassium fluoroborate, boric anhydride, and sulfuric acid methods, there are also methods for preparing boron trifluoride industrially, such as borax, fluorite, and sulfuric acid. Nicotinic acid method. The boron trifluoride generated is complexed with diethyl ether. Add fuming sulfuric acid and borax into the reaction kettle, react with stirring for 3 hours, then cool down to below 80°C, stop stirring and add fluorite powder. The generated boron trifluoride enters the complexing kettle, and the ether gas evaporated from the ether vaporizer also enters the complexing kettle and performs gas phase complexation with boron trifluoride. The complex product is distilled and refined in a still, and the fraction between 124 and 126°C is taken as the product. The ether recovered during the complexation and distillation process can be recycled in the process.
Purpose
Used as a catalyst for synthetic rubber, resin and paint making, etc.; used as a catalyst for hydrocarbonization and condensation reactions in organic synthesis (such as butadiene rubber, polyformaldehyde, coumaron, synthetic resin, etc.), and also used as It is a basic raw material for manufacturing boron hydrogen high-energy fuel or extracting isotope boron, and is also used as an epoxy resin curing agent;
It is used as a general analytical reagent and as a catalyst for alkylation and condensation reactions in organic synthesis. It is used as a catalyst for the synthesis of butadiene rubber, condensation reactions and organic synthesis reactions such as Comarone synthetic resin. It can also be used as raw material for manufacturing borane and used in the field of national defense science.


