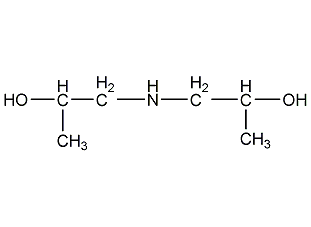
Structural formula
| Business number | 032J |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H15NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 133.19 |
| label |
Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine, 2,2′-dihydroxydipropylamine, 1,1′-Iminodi-2-propanol, 2,2′-dihydroxydipropylamine, N,N-diisopropanolamine, Bis(2-propanol)amine, Di(2-hydroxy-n-propyl) amine, 1,1′-Iminodi-2-propanol, fiber additives, tanning agent, pesticides, Absorbent for acid gases, emulsifier |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-97-4
MDL number:MFCD00004531
EINECS number:203-820-9
RTECS number:UB6600000
BRN number:605363
PubChem number:24848959
Physical property data
1. Properties: white crystalline solid with an ammonia-like odor. [1]
2. pH value: 8~10 (1% solution) [2]
3. Melting point (℃): 42[3]
4. Boiling point (℃): 249[4]
5. Relative Density (water=1): 0.99[5]
6. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.59[6]
7. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.003 (42℃)[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.82[ 8]
9. Flash point (℃): 126.7 (OC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃) :374[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 9.8[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%) %): 1.2[12]
13. Solubility: miscible with water, miscible in ethanol, slightly soluble in toluene, insoluble in hydrocarbons. [13]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14] LD50: 6720mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation[15]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild irritation (open irritation test) ;
Rabbit eye: 50mg, severe irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16]
LC50: 1100mg/L (24h) (goldfish, static ); 1000mg/L (48h) (high body yarrow)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non Biodegradability[17] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm 3, the degradation half-life is 4h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 42.62
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 170.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 373.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/ cm): 23.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.89
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 60.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 2
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[18] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, strong acids
3. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heating
4 .Hazards of aggregation[21] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
The reaction between propylene oxide and ammonia produces mono-isopropanolamine, which then reacts with propylene oxide to produce di- and tri-isopropanolamine. After mixing propylene oxide and ammonia, they are preheated to the reaction temperature and enter the reactor for reaction. The reaction product is first stripped to remove ammonia and water, and the ammonia is recycled. Then, the crude isopropanolamine is sent to a vacuum distillation system to fractionate monoisopropanolamine, diisopropanolamine and triisopropanolamine into pure products. When there is a large excess of propylene oxide in the raw material ratio, the proportion of triisopropanolamine in the resulting product increases.
Purpose
1. Used to remove hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide from natural gas and refinery gas, and used as fiber additives, tanning agents, pesticides, cutting oil, etc. Diisopropanolamine is used as an absorbent for acidic gases, such as to absorb CO2 and H2S in natural gas and petroleum refining gas, to remove CO2 from syngas in the ammonia industry, and to concentrate CO2 in dry ice production. It is also used as a neutralizing agent for metal annealing, inert gas manufacturing, and electrophoretic coatings. In terms of emulsifier, this product is used in fiber additives, tanning agents, pesticides, cutting oils, coatings and wax products. Diisopropanolamine reacts with fatty acids to form fatty acid amides and lipids, which are used as active ingredients in shampoos.
2. Used as emulsifier. And for fabric treatment, etc. [23]


