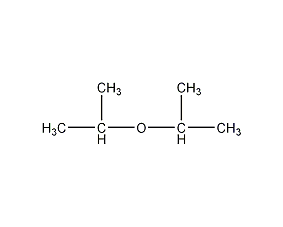
Structural formula
| Business number | 02WL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H14O |
| Molecular weight | 102.17 |
| label |
diisopropyl ether, diisopropyl ether, isopropyl ether, isopropyl ether, 2-Isopropoxypropane, Isopropyl ether, 2-Isopropoxypropane, iso-propyletyer, Solvent for waxes and resins, gasoline blending agents, stabilizer, Anesthetic, Extracting agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-20-3
MDL number:MFCD00008880
EINECS number:203-560-6
RTECS number:TZ5425000
BRN number:1731256
PubChem number:24863910
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -85.9[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 68~69[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.73[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.52[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 16.00 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4016.5[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 228[ 8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.88[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.56[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -28 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition Temperature (℃): 443[12]
13. Explosion limit (%): 22[13]
14 .Lower explosion limit (%): 1.4[14]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, benzene, and chloroform. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.329
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.379
18. Flash point (ºC, open): -9.4
19. Flash point (ºC, closed): -27.8
20. Fire point (ºC): 443
21. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg): 28.55
22. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 29.17
23. Heat of fusion (KJ /kg): 107.96
24. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 11.03
25. Heat of formation (KJ/kg): 3520
26. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 2.20
27. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 30ºC, constant pressure): 2.21
28. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00144
29. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.265
30. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 386
31. Critical compression factor: 0.263
32. Eccentricity factor: 0.338
33. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 14.354
34.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.022×1010
35. van der Waals volume (cm3�The water generated by the reaction is separated at the reflux side. When water is no longer generated, the reaction ends:
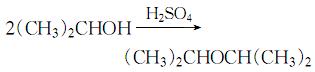
After cooling down, pour the reaction solution into cold water, let it stand and separate into layers, and discard the water layer. The oil layer is first washed with water to remove unreacted alcohol, then potassium permanganate solution is added to remove the olefins and washed with water, the peroxide is removed with ferrous sulfate aqueous solution and then washed with water, and then the acid contained is neutralized with sodium hydroxide solution and washed with water. to neutrality, let it stand for stratification, discard the water layer, dry and dehydrate the ether layer with anhydrous calcium chloride, filter out the solid desiccant, and distill under normal pressure to collect the fraction between 67 and 69°C, which is the finished product isopropyl ether. High-purity isopropyl alcohol can be obtained by using a wastewater solution containing 70% isopropyl alcohol, which is first azeotropically distilled with benzene to remove water, and then filtered through a three-layer polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with pore sizes of 0.8μm, 0.45μm and 0.2μm after cooling. . The product contains 99.9% isopropyl alcohol, 0.1% water, 0.4×10-6 Ca and 0.01 to 0.09×10-6 other cationic impurities (such as K , Mg, Cr, Fe and Na).
Purpose
1. Used as standard material, solvent and extractant for chromatographic analysis, and also used in organic synthesis. Isopropyl ether has a higher boiling point than diethyl ether and acetone, is less volatile, and has less solubility in water. Therefore, it is easier to use industrially than diethyl ether. In addition to being used as a solvent for grease, wax, mineral oil, some natural resins, ethyl cellulose, etc., it is also used for the concentration and recovery of dilute solutions of acetic acid or butyric acid. A mixture with isopropyl alcohol is used for dewaxing grease and deoiling wax.
2. Diisopropyl ether is a good solvent for animal, vegetable and mineral oils and fats, and can be used to extract nicotine from tobacco. It is also a good solvent for paraffin and resin. In industry, diisopropyl ether is often used to extract nicotine from tobacco. Mixed with other solvents for dewaxing of paraffin-based oils. As a solvent, it is also used in pharmaceuticals, smokeless gunpowder, coatings and paint cleaning. Diisopropyl ether has a high octane number and anti-freeze properties, and can be used as a gasoline blending agent. This product easily forms peroxide and explodes when shaken. Para-benzylaminophenol is often added as a stabilizer. The anesthetic effect of diisopropyl ether is lighter than that of diethyl ether, but the duration of anesthesia is longer.
3. Used as a solvent, and also used for the concentration and recovery of dilute solutions of acetic acid or butyric acid. [26]


