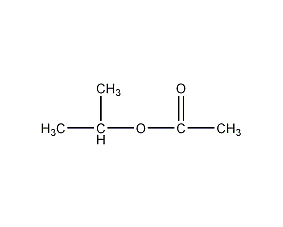
Structural formula
| Business number | 02WM |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H10O2 |
| Molecular weight | 102.13 |
| label |
Isopropyl acetate, 1-methylethyl acetate, Acetic acid-1-methylethyl ester, 2-Acetoxy-propane, Essigsaeure-isopropyleste, dehydrating agent, drug extractant |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-21-4
MDL number:MFCD00008877
EINECS number:203-561-1
RTECS number:AI4930000
BRN number:1740761
PubChem number:24878222
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with fruity aroma. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -73[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 88.4[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.87[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.52[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 5.8 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2236.6[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 265[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.65[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.02 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 2 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) ): 460[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 7.8[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.8[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and esters. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.569
17. Flash point (ºC, closed): 4.44
18. Flash point (ºC, open): 11
19. Fire point (ºC): 460
20. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, b.p.): 33.08
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): 484.83
22. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 2799.7
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ/( kg·K), constant pressure): 2.18
24. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00132
25. Critical density (g· cm-3): 0.297
26. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 344 p>
27. Critical compression factor: 0.258
28. Eccentricity factor: 0.355
29. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3 )0.5: 17.120
30. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.130×10 9
31. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 62.990
32. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2907.04
33. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -489.65
34. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2869.80
35. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -526.85
36. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol -1·K-1): 196.6
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 6750mg/kg���rat oral); >20ml (17400mg)/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 50600mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 8h)
2. Irritation [17] Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18] IC50: 165~1400mg/L (72h) (algae)
2. Biological Degradability [19] In the screening test, stable sewage sludge was used. After 5, 10, and 40 days, the degradation rate was 12.7%, 40%, and 49.1% respectively.
3. Non-biodegradability[20] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 4.7h (theoretical).
When the pH value is 7 and 8, the hydrolysis half-life is 2.4a and 88d respectively (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [21] This substance is harmful to the environment and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.94
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 114.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 253.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 10.68
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 66.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Similar to propyl acetate, it gradually hydrolyzes into acetic acid and isopropyl alcohol in the presence of water. During the photochlorination reaction, chloroisopropyl acetate is produced. Among them, the yields of 1-chlorosubstituted products and 2-chlorosubstituted products are equal. The Friedel-Crafts reaction with benzene catalyzed by aluminum trichloride is similar to propyl acetate. When heated to 350°C, it cleaves to produce acetic acid and propylene.
2. Stability[22] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[23] Strong oxidants, alkalis, acids
4. Polymerization hazard[24] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Add acetic acid, isopropyl alcohol and concentrated sulfuric acid to the enamel kettle, heat and reflux with stirring for more than 10 hours, cool down and neutralize with sodium bicarbonate or saturated sodium carbonate solution to pH 7~8, wash with saturated salt water solution, and then wash with water. After standing to separate the water layer, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate. After filtering, add it to a distillation tower for rectification. Collect the fractions between 85 and 95°C, which is the finished product.
Refining method: often contains impurities such as water, acetic acid and isopropyl alcohol. During purification, add 50g potassium carbonate to 100mL of ester and shake thoroughly to remove acid. Then wash with concentrated calcium chloride solution to remove alcohol, dry with anhydrous calcium chloride for 1 day and night and then distill.
Purpose
1. It is mainly used as a solvent for coatings, printing inks, etc. It is also a commonly used dehydrating agent in industry, an extractant and a spice component in pharmaceutical production.
2. Used as an extraction agent for pharmaceuticals, used to make flavors, and also used as solvents and reagents for coatings, etc. [26]


