Background[1][2]
4-Bromobenzoic acid, also known as p-bromobenzoic acid, is white or light pink crystal. 4-Bromobenzoic acid is an important fine chemical that can be used as a raw material for spices, an intermediate for 4-bromobenzoate, and a standard for measuring strontium and organic trace analysis for measuring carbon, hydrogen and bromine.
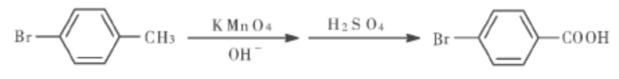
There are currently two main methods for producing 4-bromobenzoic acid. One is to produce p-bromobenzoic acid by oxidizing p-bromotoluene with potassium permanganate. The cost is too high and the yield is only 80%; the other is The method is to react bromobenzene with acetyl chloride to generate 4-bromoacetophenone, and then react 4-bromoacetophenone with sodium hypochlorite to generate 4-bromobenzoic acid. This method has many reaction steps and serious pollution. In view of the problems existing in the above-mentioned existing technologies, it is urgent to research and develop a new process for preparing 4-bromobenzoic acid with less pollution, low cost and high yield.
Apply[2][3][4][5]
4-Bromobenzoic acid is an important fine chemical that is used as an analytical reagent and as an intermediate in organic synthesis and as an intermediate for dyes and medicines. Examples of its application functions are as follows:
1. Synthesis of anidulafungin intermediate p-pentyloxyterbenzoic acid.
Anidulafungin is an echinocandin antifungal drug used to treat candidemia, other types of Candida infections (abdominal abscess, peritonitis) and esophageal Candida infections in adults. The drug was developed and marketed by Pfizer. It was first approved for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on February 17, 2006, and then by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) on September 20, 2007. , marketed by Pfizer in the United States and Europe.
The method includes the following steps: using N,N-dimethylformamide as a solvent in an alkaline aqueous solution, using a palladium catalyst to catalyze, and adding 4-bromobenzoic acid and 1,4-phenylenediboronic acid pinacol. Using ester and 4-n-pentoxybromobenzene as raw materials, a SUZUKI coupling reaction was performed to obtain the target product anidulafungin intermediate—p-pentyloxyterbenzoic acid. The raw materials used in the preparation method of the present invention are all industrialized products already on the market. The raw materials are easy to obtain, the steps are short, and the reaction conditions are mild and controllable, which greatly reduces the three waste problems generated in the production process of the product and is in line with the green concept of today’s society. Chemical environmental protection requirements.
2. Synthesis of ethyl 4-(9-(β-naphthalene)-10-anthracenyl)benzoate.
Add 9-(β-naphthalene)-10-bromoanthracene into the reaction vessel, add the solvent, lower the temperature to -78°C under nitrogen protection, add n-butyllithium, stir, and then add triisopropyl borate. Then stir at room temperature and acidify with hydrochloric acid to obtain 9-(β-naphthalene)-10-anthraceneboronic acid; add 9-(β-naphthalene)-10-anthraceneboronic acid and ethyl 4-bromobenzoate into the reaction vessel, add catalyst and Acid binding agent, after the reaction vessel is evacuated and nitrogen is circulated, the solvent is added, the reaction is carried out at the boiling point of the solvent, and the target product is obtained by column chromatography separation.
The invention has low raw material cost and mild reaction conditions. It lays the foundation for the construction of more blue luminescent materials with excellent performance, and provides more possibilities for the application of anthracene compounds as semiconductor materials in organic electroluminescent devices and organic photoconductors.
3. Synthesis of p-bromoxynil.
P-bromoxynil is a white crystal with a melting point of 112-114°C and a boiling point of 236°C. p-bromoxynil can be used as pharmaceutical intermediates, pigment intermediates, pesticide intermediates and pharmaceutical intermediates. Its emulsion has good control effect on broad-leaf weeds in garlic fields and is safe for crops.
The preparation method is to use phosphorus oxychloride, 4-bromobenzoic acid and 1,1-diphenylethane, stir and mix, introduce ammonia until the solution becomes alkaline, use nitrogen to replace the internal mixed gas reaction and then cool it , filter, separate and then use an alkali solution prepared with sodium hydroxide, stir, separate and combine again, then add 35% hydrochloric acid for reaction, and the product obtained is the finished product of p-bromoxynil, which is packaged and stored in the warehouse. The beneficial effects are that the preparation is convenient and simple, environmentally friendly and pollution-free, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the equipment investment is small, the purity is high, and the operation is easy. The prepared p-bromoxynil has good use effect and is safe and reliable.
4. Synthesize a pemetrexed disodium intermediate.
The intermediate is (2-{4-[3-(2,4-diamino-6-oxy-1,6-dihydro-pyrimidin-5-yl)-3-[1,3 ]dioxolane-2-yl-propyl]benzylamine}sodium glutarate). In the synthetic route of this intermediate, 4-bromobenzoic acid or 4-iodobenzoic acid and L-glutamic acid diethyl ester are first subjected to a condensation reaction, and then through Hack reaction, the bromine at the 4-position is substituted to form butyraldehyde at the 4-position. , and then selective bromination and conversion into 2-bromobutyraldehyde. After that, the aldehyde group is protected by the condensation reaction of the aldehyde group and ethylene glycol, and the pyrimidine ring is further synthesized to obtain the intermediate.
The intermediate undergoes an acid hydrolysis ring-closure reaction and a sodium hydroxide salt formation to obtain pemetrexed disodium. The method for preparing pemetrexed disodium has high yield, low cost and simple operation, and is suitable for industrial production.
Preparation[6][7]
Method 1: A method for preparing 4-bromobenzoic acid, which uses p-bromotoluene as the starting material, glacial acetic acid as the solvent, and oxygen as the oxidant, and uses liquid phase oxidation method to catalytically oxidize p-bromotoluene under the action of a catalyst , control the reaction temperature to 75~85°C, end the reaction when the content of p-bromotoluene in the reaction system is less than 0.5wt% of the initial content, then cool and filter to obtain 4-bromobenzoic acid crude product and filtrate, and then use the 4 – The crude bromobenzoic acid product is further purified to obtain the finished product.
The specific steps of the crude product purification process are as follows:Mix the product with water to obtain a crude mixture. Then use alkali solution to adjust the pH of the mixture to 8 and raise the temperature to 70-90°C. Add activated carbon to stir for decolorization and then filter. The filtrate is heated to 80-100°C and adjusted with 10% dilute sulfuric acid. The pH of the mixture is 2. Cool to room temperature and then filter. Collect the solids and dry them to obtain the finished product. The melting point of the finished product of 4-bromobenzoic acid is 252-254°C, and the purity is more than 99%.
![]()
Method 2: Phase transfer catalytic synthesis of p-bromobenzoic acid. Add p-bromotoluene, catalyst TEBA, and water to the three-necked flask in sequence, turn on the reflux condensation device and stirrer. Heat the water bath, and when the water bath temperature rises to a certain temperature, add potassium permanganate in batches to the three-necked flask. After that, the temperature-controlled reaction time is about 2.5 h. When the reaction is completed, filter while it is hot to remove the precipitate generated during the reaction. The filter cake is washed twice continuously with boiling water, and the washing liquid and the filtrate are combined. If the color of the liquid is purple, then Add ethanol, heat to decompose potassium permanganate, then filter and wash.
Concentrate the combined filtrate, add 50% sulfuric acid for acidification after cooling, and a white precipitate will appear. After cooling, suction filtration, the filter cake is washed with cold distilled water, placed in an infrared constant temperature drying oven for drying, and weighed. Melting point: 251 ~ 256 ℃.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201810447513.5 A preparation method of 4-bromobenzoic acid
[2] CN201711093364.9 Preparation method for one-step synthesis of anidulafungin intermediate p-pentyloxyterbenzoic acid
[3] Preparation method of CN201610682347.84-(9-(β-naphthalene)-10-anthracenyl)benzoic acid ethyl ester
[4] CN201410255874.1 A production process for the synthesis of p-bromoxynil
[5] CN200910115429.4 A pemetrexed disodium intermediate, its preparation method and a method for preparing pemetrexed disodium from the intermediate
[6] CN201810447513.5 A preparation method of 4-bromobenzoic acid
[7] Liu Rong, Qi Xiaolu, Zhi Sanjun. Research on the synthesis of p-bromobenzoic acid by phase transfer catalysis[J]. Journal of Huaiyin Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 10(4): 316-318.


