[Background and Overview][1][2]
As a common clinical condition and a high incidence in my country, the exploration of treatment options for hypertension has received more attention. Hypertension has the characteristics of high incidence and lifelong persistence. During the course of the disease, blood pressure levels will increase to varying degrees, which will have a greater impact on physical health. Because the disease lasts for a long time, medical staff recommend that patients take medication for a long time to lower and stabilize blood pressure and control the development of the disease, which can fundamentally reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and kidney disease. Nifedipine is often used in the clinical treatment of hypertension. This drug belongs to the calcium ion antagonist class and is a common clinical drug.
Nifedipine, chemical name is 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro- 3,5-Dimethylpyridinedicarboxylate is a calcium channel blocker. Its tablets are mainly used clinically to treat angina pectoris and hypertension, but existing nifedipine tablets generally have poor dissolution. Pharmacokinetics shows that the biological half-life of the drug is relatively short and the plasma concentration fluctuates greatly. Therefore, the common preparation of nifedipine can reflexively cause adverse reactions such as increased heart rate, activation of the sympathetic nervous system, and is not conducive to the control of myocardial ischemia and heart failure. Moreover, it requires frequent administration and is not suitable for long-term treatment of hypertension. , and is not suitable for use in hypertensive emergencies, acute myocardial infarction or acute coronary syndrome, making it difficult to meet the medication needs of patients.
In order to reduce the frequency of medication and make it safer, experts at home and abroad suggest that it is best to use sustained-release preparations for nifedipine, especially long-acting sustained-release tablets that maintain blood concentration for a longer period of time. Nifedipine sustained-release tablets rank second in terms of clinical efficacy, side effects, and treatment costs; nifedipine controlled-release tablets have the best clinical effect, the lowest side effects, the lowest incidence of adverse reactions, and a better prognosis. This drug has the most outstanding clinical efficacy and prognostic effect, but among the three drugs, nifedipine controlled-release tablets have the highest treatment cost. In clinical treatment, medical staff must consider many aspects such as the actual degree of illness, course of disease, personal wishes, and family economic status to formulate the most targeted treatment plan for the patient.
[Indications][3]
1. Used for hypertension. Because of its ability to calm the liver and subdue yang, it has a good effect on various diseases caused by high blood pressure, such as headaches, dizziness, etc.
2. Used for blood stasis syndrome of coronary heart disease and refractory congestive heart failure. Taking its effect of activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis, it is effective in treating palpitations, chest tightness, etc. It can unblock the blood vessels and relieve water and dampness, and eliminate swelling and fullness.
3. Used for various types of chest pain. Its function of unblocking meridians and relieving pain is applied to chest numbness and tingling, and the curative effect is remarkable.
[Specifications][4]
Nifedipine tablets: 10 mg × 100 (× 24, × 96) tablets/box (bottle); 5 mg × 100 (× 24, × 60) tablets/box (bottle).
Nifedipine capsules: 5mg×10 (×12) capsules/box (bottle), 10mg×10 (×12) capsules/box (bottle).
Nifedipine soft capsules/capsules: 10mg×60 capsules/box (bottle), 5mg×60 capsules/box (bottle).
【Usage and Dosage】[4]
Oral sustained-release dosage form: It takes effect in 15 minutes after oral administration, peaks in 1 to 2 hours, and lasts for 4 to 8 hours. Sublingual administration takes 2 to 3 minutes to take effect and peaks at 20 minutes. The general starting dose is 10 mg once, tid; the usual maintenance dose is 10 to 20 mg once, tid. For patients with obvious coronary artery spasm, 20 to 30 mg can be taken once tid or qid. The maximum single dose is 30 mg and the maximum daily dose is 120 mg. In an emergency, 10 mg can be taken by chewing or sublingually.
[Pharmacological effects][5]
1. It has the effect of inhibiting Ca2+ influx, can relax vascular smooth muscle, dilate coronary arteries, increase coronary blood flow, improve myocardial tolerance to ischemia, and can also expand peripheral small arteries, reducing peripheral vascular resistance, thereby lowering blood pressure. It does not affect blood pressure when dilating coronary arteries in small doses, making it a better anti-angina drug. Used as an antihypertensive drug, it does not have the side effects of water and sodium retention and edema that are common with general vasodilators.
2. It has the effect of relieving asthma. Studies have confirmed that nifedipine can reduce or prevent tracheospasm induced by exercise, cold air, allergens, histamine and other factors. Its mechanism of action in treating asthma is: ① Inhibiting smooth muscle contraction. ②Inhibit the release of mast cell mediators. ③ Affects the synthesis of histamine and slow-reacting substances. ④Inhibit smooth muscle choline receptors. It can be used for the prevention and treatment of asthma and asthma patients with angina pectoris or hypertension.
[Pharmacokinetics][5]
Nifedipine is well absorbed after oral administration, takes effect in 10 minutes, reaches maximum effect in 1 to 2 hours, and lasts for 6 to 7 hours. Sublingual administration is more rapid than oral administration. The antihypertensive effect occurs within 10 minutes of spray administration. The effect is most significant after 1 hour, and the blood pressure rises after about 3 hours. Intravenous injection can reduce blood pressure by 21% to 26% within 10 minutes. The peak plasma concentration is between 1.6 and 4.0 hours after oral administration of the sustained-release tablet, and it lasts for 12 hours after taking it once. After taking the controlled-release tablet orally, the blood concentration reaches the plateau in about 6 hours and remains there for 24 hours.
[Adverse reactions][3]
For those who take it for the first time, their heart pulse will be warm and their blood will flow smoothly, so their face will be flushed, their heart yang will be invigorated, and their blood will flow smoothly.If the movement is forceful, palpitations and sinus tachycardia may occur. In some cases, due to phlegm and blood stasis, it becomes warm and turns into water evil, which blocks the tongue collaterals and causes numbness at the base of the tongue. If the body fluid is not distributed, the mouth will be dry, and if the body fluid does not circulate through the meridians and leak out, sweat will occur. If the water evil is blocked, the clear yang will not rise. If the turbid yin does not decrease, there will be headache, nausea, loss of appetite, etc. Occasionally, when moisture evaporates, jaundice develops, glutamic acid oxaloacetate aminotransferase and glutamic acid propionic acid aminotransferase increase, and blood pressure drops; when moisture accumulates, lower limbs become edematous.
[Drug Interaction][4]
(1) Nifedipine may increase the blood concentration of digoxin, so when used together with digoxin, attention should be paid to adjusting the dose of digoxin.
(2) Nifedipine can increase the blood concentration of phenytoin.
(3) Nifedipine can increase the elimination of quinidine and reduce the antiarrhythmic effect of quinidine.
(4) The combined use of nifedipine and prazosin can cause acute hypotension.
[Notes][4]
(1) Use with caution during lactation. Breastfeeding should be suspended if used.
(2) The dosage should be gradually adjusted based on the control of angina pectoris and the patient’s tolerance. Excessive dosage can lead to hypotension.
(3) Use with caution in patients with severe aortic stenosis.
(4) The dose should be reduced in case of severe hepatic insufficiency.
(5) The elderly should start with a small dose.
(6) The dosage should be reduced slowly after discontinuing medication.
(7) Can affect the ability to drive and operate machinery.
(8) Do not use in combination with rifampicin.
【Preparation】[6]
A method for preparing nifedipine is: in the same reactor, first make o-nitrobenzaldehyde (IV) and methyl acetoacetate (III) generate benzylidene under the catalysis of pyridine carboxylate Base compound (II):
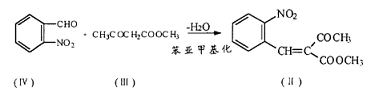
The generated benzylidene compound (II) is condensed with methyl acetoacetate and ammonia to form nifedipine without separation:
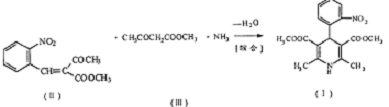
[Main reference materials]
[1] Fan Yuwu. Comparative analysis of the clinical effects of different dosage forms of nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension[J]. Medicine and Health (Abstract Edition), 2017 (06): 00050-00050.
[2] Xu Chengmiao; Fang Nanping; Yang Guodong; Yan Liyong; Zhou Jun; Ma Hailing. A nifedipine sustained-release tablet and its preparation method. CN201310278671.X, application date 2013-07-02
[3] New family of traditional Chinese medicine – chemical traditional Chinese medicine
[4] National Manual on Essential Medicines
[5] Clinical Practical Drug Manual
[6] Li Shifa; Ni Zhong; Jia Lisen; Fang Hongbin. Preparation method of nifedipine. CN01139968.6, application date 2001-11-22


