Background and overview[1]
Diphenyl carbonate (DPC) is an important organic compound and the basic raw material for the non-phosgene synthesis of polycarbonate. In recent years, polycarbonate has a wide range of applications due to its good mechanical, optical, and electronic properties. As a result, the research and development of DPC has gradually become a focus of attention. At present, the main methods for synthesizing DPC using non-phosgene methods include transesterification and oxidative carbonylation. Among them, phenol and dimethyl oxalate (DMO) are transesterified to synthesize DPC by transesterifying phenol and DMO to synthesize diphenyl oxalate (DPO), and DPO is further decarbonylated to generate DPC. In this method, the by-products methanol and CO are easily separated from the reaction system, which avoids the problem of forming an azeotrope between the by-product methanol and the raw material dimethyl carbonate in the synthesis of DPC process by transesterification of dimethyl carbonate and phenol, and reduces separation Difficulty. At the same time, the normal pressure reaction is adopted, the reaction conditions are mild, and the catalyst is cheaper and easier to obtain than the phenol oxidative carbonylation synthesis DPC method, so it is a promising process route. .
Preparation[1-3]
1) Phosgene method
The phosgene method is the earliest method for synthesizing DPC. First, phosgene and phenol are reacted in a NaOH solution to form phenyl chloroformate. The phenyl chloroformate then reacts with phenol to synthesize DPC. The reaction equation is as follows:
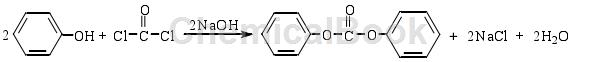
After decades of development, the phosgene synthesis process for DPC has become very mature and is the main method for industrial production of DPC so far. In recent years, there are still a few reports on the improvement of the phosgene method. For example, using TiO2/Al2O3 as a catalyst, DPC with a yield of 50.7% was obtained at 150°C. Although phosgene has excellent reactivity, it does not meet the requirements of environmental protection due to its high toxicity. Therefore, with the gradual increase of people’s awareness, since the 1970s, non-phosgene synthesis of DPC has been carried out at home and abroad. Research on new processes, which mainly include oxidative carbonylation and transesterification.
2) Phenol oxidative carbonylation method
The oxidative carbonylation method is a method of directly synthesizing DPC using CO, O2 and phenol as raw materials under the action of a catalyst. The reaction equation is as follows:
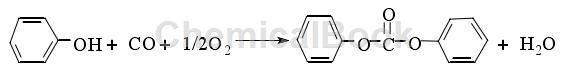
The oxidative carbonylation reaction is generally carried out at 0.4 to 9MPa and 50 to 150°C. The catalytic system generally uses palladium compounds, and its research began in the late 1970s. This method has the advantages of no pollution, no need for solvents, and no generation of toxic salts, and is a popular research direction at present. However, the reaction conditions of this route are relatively harsh, generally requiring high temperature and high pressure, and the catalyst is expensive and complex, with low reaction activity and some side reactions. So far, the main catalysts reported in the literature for the synthesis of DPC by oxidative carbonylation are Group VIII metals or their compounds, among which Pd or Pd compounds are the focus of research. Because the catalyst system is complex, expensive and has low activity; and phenol is easily oxidized, and the water generated by the reaction is difficult to remove, the synthesis of DPC by oxidative carbonylation is currently limited to laboratory research, and there have been no industrial reports.
3) Lewis acid catalyzed synthesis of diphenyl oxalate
In the process of transesterification of phenol and DMO to generate DPO, phenol and DMO are first transesterified to generate methyl phenyl oxalate (MPO), and then MPO undergoes a disproportionation reaction to generate DPO. The reaction equation is as follows:
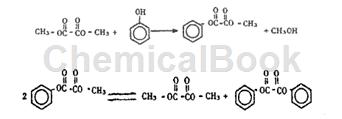
A 250mL three-necked flask is equipped with a sealed stirrer, thermometer and reflux condenser. Add a certain amount of phenol, DMO and catalyst under normal pressure, stir and raise the temperature. Pour 80°C constant-temperature circulating water into the reflux condenser tube, and collect the distillate in the cold trap. The outlet of the cold trap is connected to a three-way valve, and a gas sample is taken for analysis at the three-way valve. After the reaction is completed, the solid catalyst is removed by filtration under reduced pressure, and the filtrate is a mixture of the reaction product and unreacted raw materials. The composition of the reaction solution, liquid distillate and gas sample was determined by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and gas chromatography. Using weakly acidic TS-1 molecular sieve as the catalyst, the total selectivity of MPO and DPO was 99.2%. Using strong acid AlCl3 as catalyst, the selectivity of anisole reaches 60.4%.
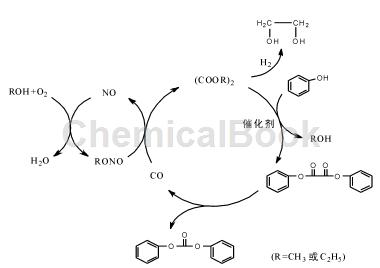
4) Transesterification method
Dialkyl oxalate (mainly dimethyl oxalate and diethyl oxalate) and phenol are transesterified to form diphenyl oxalate, and then diphenyl oxalate is decarbonylated to form diphenyl carbonate. The operating conditions of this process are relatively mild, the product is easy to separate, and the generated CO can be recycled into the synthetic raw material dialkyl oxalate, effectively achieving atom economy and greening the process, which has attracted widespread attention. In addition, this process route uses the intermediate dialkyl oxalate produced by the “coal-to-ethylene glycol” process as raw material to synthesize diphenyl carbonate, which expands the downstream products of coal chemical industry, is suitable for my country’s national conditions, and is of great significance.
Main reference materials
[1] Study on the reaction of Lewis acid catalyzed synthesis of diphenyl oxalate
[2] Molybdenum-titanium solid acid catalyst catalyzes transesterification to synthesize diphenyl oxalate
[3] Research progress on catalysts for preparing diphenyl oxalate by transesterification method


