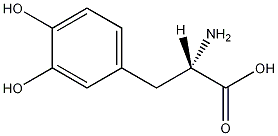
Structural formula
| Business number | 01AT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H11NO4 |
| Molecular weight | 197.19 |
| label |
3-hydroxy-L-tyrosine, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine, L-3-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)aniline, 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine, 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine L-3-Hydroxytyrosine, Levodopa, Amino acid drugs |
Numbering system
CAS number:59-92-7
MDL number:MFCD00002598
EINECS number:200-445-2
RTECS number:AY5600000
BRN number:2215169
PubChem number:24277914
Physical property data
1. Properties: White flake or needle crystals or crystalline powder. Odorless. Tasteless.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 276~278℃ (284~286℃) (decomposition)
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): 276~278℃ (284~286℃) (decomposition)
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Not determined
12. Saturation vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Not determined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Not determined Determined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/water ) Log value of distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined Confirm
19. Solubility: It is easily oxidized in the air when humid and becomes darker in color. Easily soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and formic acid, soluble in water (66mg/40ml), almost insoluble in ethanol, benzene, chloroform and ethyl acetate.
Toxicological data
None yet
Ecological data
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 49.25
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 134.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 401.8
4. Surface tension���dyne/cm): 80.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 19.52
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 4
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: 18
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 104
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 209
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 1
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
L-dopa is an intermediate product of catecholamines formed from tyrosine, which is the precursor of dopamine. About 95% of the L-dopa absorbed into the blood is decarboxylated by dopa decarboxylase in peripheral tissues to form catecholamines, which are difficult to pass through the blood-brain barrier and cause many adverse reactions. Only 1% ofL-dopa enters the cerebral circulation and reaches the central nervous system, where it is converted into catecholamines to exert therapeutic effects. It has no significant pharmacological effect on its own, but exerts its therapeutic effect indirectly through catecholamines.
Storage method
This product should be stored in a dry and dark place filled with argon gas.
Synthesis method
![]() 1. Amino acids can be extracted from Mucuna sempervirens Hemsl seeds—— Levodopa. The extraction method is as follows: crush the quinoa beans and extract them three times at room temperature with a mixture of 30% ethanol and 0.1% acetic acid, each time for 24 hours. Filter to get the extract. Concentrate the extract under reduced pressure (21.3kPa) to precipitate crystals, let it stand overnight at 0-10°C, filter, and obtain crude levodopa. Dissolve the crude product with 1N hydrochloric acid, add activated carbon to filter, add a small amount of vitamin C to the filtrate and neutralize it to pH 3.5 with 2N ammonia water, and precipitate a large number of crystals. Let stand at 0-10℃ for 4 hours and filter. The filter cake was washed twice with distilled water containing a small amount of vitamin C, and rinsed and dehydrated once with acetone. Dry at 60-70℃ to obtain levodopa. Based on soy flour, the yield is about 2%. Levodopa can also be obtained by oxidation of L-tyrosine. Dissolve tyrosine in formic phosphoric acid, raise the temperature to 40°C and keep it for 12 hours, and dilute it with 20 times of distilled water. The diluted liquid is passed through a strongly acidic styrene-based cation exchange resin to adsorb unreacted tyrosine, and then undergoes post-chilling operations to obtain the finished product.
1. Amino acids can be extracted from Mucuna sempervirens Hemsl seeds—— Levodopa. The extraction method is as follows: crush the quinoa beans and extract them three times at room temperature with a mixture of 30% ethanol and 0.1% acetic acid, each time for 24 hours. Filter to get the extract. Concentrate the extract under reduced pressure (21.3kPa) to precipitate crystals, let it stand overnight at 0-10°C, filter, and obtain crude levodopa. Dissolve the crude product with 1N hydrochloric acid, add activated carbon to filter, add a small amount of vitamin C to the filtrate and neutralize it to pH 3.5 with 2N ammonia water, and precipitate a large number of crystals. Let stand at 0-10℃ for 4 hours and filter. The filter cake was washed twice with distilled water containing a small amount of vitamin C, and rinsed and dehydrated once with acetone. Dry at 60-70℃ to obtain levodopa. Based on soy flour, the yield is about 2%. Levodopa can also be obtained by oxidation of L-tyrosine. Dissolve tyrosine in formic phosphoric acid, raise the temperature to 40°C and keep it for 12 hours, and dilute it with 20 times of distilled water. The diluted liquid is passed through a strongly acidic styrene-based cation exchange resin to adsorb unreacted tyrosine, and then undergoes post-chilling operations to obtain the finished product.
2.Artificial synthesis
Purpose
1. Used for biochemical research. Substrate of tyrosinase. medicine. 2. Levodopa is currently one of the effective drugs for the treatment of shaking paralysis. It is one of the precursors for the synthesis of norepinephrine, dopamine, etc. in the body and is a catecholamine. Levodopa can enter the brain through the blood-brain barrier and be decarboxylated by doma decarboxylase into dopamine to exert its effects. But the effect is slow and the side effects are serious.


