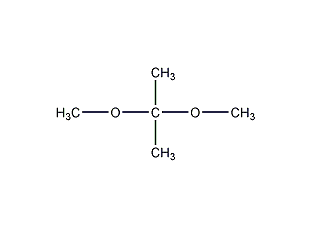
Structural formula
| Business number | 01M4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H12O2 |
| Molecular weight | 104.15 |
| label |
2,2-methoxypropane, Acetone dimethyl acetal, 2,2-methoxypropane, dimethoxypropane, 2,2-Dimethoxy-propan, Acetone dimethyl ketal |
Numbering system
CAS number:77-76-9
MDL number:MFCD00008479
EINECS number:201-056-0
RTECS number:None
BRN number:635678
PubChem number:24893272
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent liquid [9]
2. Melting point (ºC): -47[10]
3. Boiling point (ºC): 81[11]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.85[12]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.59[13]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 8.00 (15.8℃) [14]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.380[15]
8. Flash point (ºC ): -7[16]
9. Explosion upper limit (%): 31.0[17]
10. Explosion Lower limit (%): 6.0[18]
11. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents. [19]
12. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3252.9
13. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -429.6
14. Critical temperature (ºC): 236.85
15 .Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3223.5
16. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1):-459.0
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[20] LD50: 71000mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation No information yet
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 28.66
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 123.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 265.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 21.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.36
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 18.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 44
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14.NoThe number of stereocenters of certain chemical bonds: 0
15. The number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[21] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[22] Acids, strong acids
3. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. It should be stored separately from acids, etc. and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Indirect method for synthesis of 2,2-dimethoxypropane. Process conditions for synthesizing 2,2-dimethoxypropane using ethylene glycol and acetone as raw materials via 2,2dimethyl-1,3-dioxopentane (DMD). Dichloromethane is used as the water-carrying agent and anhydrous ferric sulfate is used as the catalyst. After synthesizing DMD, it is exchanged with methanol and aluminum trichloride is used as the catalyst to synthesize DMP. The overall yield of the two-step reaction reached 60%.
Purpose
1. Used as a protective agent, condensing agent, cyclizing agent, dehydrating agent, etc., and is widely used in the synthesis of medicines, pesticides, spices, etc. It is also used as analytical reagent, drip analysis of trivalent chromium and gallium, microscope analysis, spectrum analysis reagent, cesium salt manufacturing, pharmaceutical industry, X-ray fluorescent screen manufacturing, photoelectric tube materials, etc.
2. Used in biochemical research and organic synthesis. [25]
3. This product can be used not only for the preparation of acetals, acetone compounds, isopropylidene derivatives, but also for the preparation of methyl esters of amino acids and enol ethers. , can also be used in the preparation of phosphate esters and dimethyl borate esters.
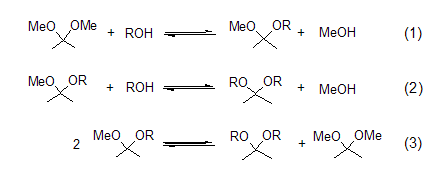
Acetal formation Through acetalization reaction, different types of acetals can be prepared from 2,2-dimethoxypropane. This reaction process involves the exchange of methoxy or ketone groups in acidic media [1]. There are three equilibrium reactions (Formula 1 to Formula 3) when 2,2-dimethoxypropane, alcohol and catalytic amounts of acid are mixed. The generated methanol is distilled off, which is beneficial to the acetal reaction. Methanol and 2,2-dimethoxypropane form a binary azeotrope, which is destroyed by the addition of an alkane solvent such as hexane or benzene.
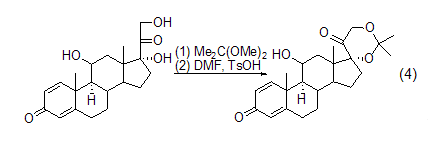
Formation of acetone compounds 2,2-Dimethoxypropane has great advantages as a protecting group. In the acid-catalyzed exchange reaction, the 21-diol group of the hydrogenated prednisone side chain 17a undergoes a cyclic acetal reaction with 2,2-dimethoxypropane to form 17a , 21-diisopropylidenedioxopregnane has a good yield (formula 4)[2]. The diisopropylidenedioxy functional group is stable to bases.
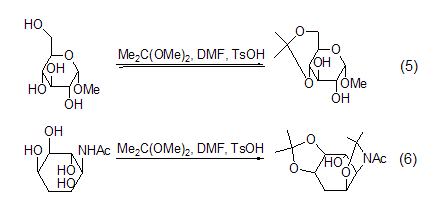
Isopropylene Derivatives 2,2-Dimethoxypropane can be used to protect hydroxyl groups. A mixture of 2,2-dimethoxypropane, DMF and a catalytic amount of p-toluenesulfonic acid is an effective pyruvate ester protector. agent, able to protect the cis-o-diequivalent hydroxyl group. Methyl α-D-pyranose reacts under the above conditions to generate methyl 4,6-O-isopropylidene-α-D-pyranose. When deoxyinositolamine is treated with the same mixed reagent, it mainly produces diisopropylidene derivatives (Formula 5, Formula 6)[3].
Esterification of amino acids Methyl esters ofamino acids can be prepared using 2,2-dimethoxypropane as a methoxy source and reaction solvent. This process can also be used to prepare fatty acid methyl esters[4].
Enol Ether Treat testosterone with 2,2-dimethoxypropane/DMF/TsOH to convert this substance into enone ether (Formula 7)[5].
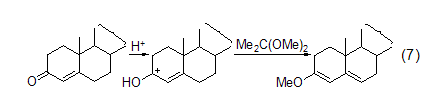
Formation of methyl hypophosphite EsterMethyl hypophosphite can be produced by reacting hypophosphorous acid with 2,2-dimethoxypropane. However, this product will further react with the generated acetone to form methyl 1-hydroxy-1,1-dimethylphosphonite (Formula 8, Formula 9)[6].
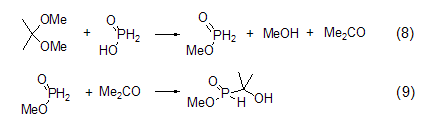
Formation of dimethyl borate EstersHeating acid, 2,2-dimethoxypropane and zinc chloride (catalyst) can produce dimethyl esters of arylboronic acids[7].
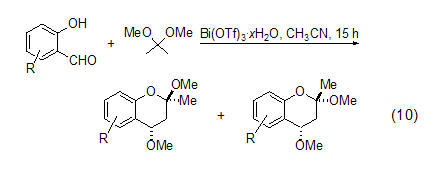
Formation of benzopyran Using bismuth compounds to catalyze the reaction of 2,2-dimethoxypropane is a hot topic in recent research. Bismuth compounds are considered to be non-toxic and green. . For example, use Bi(OTf)3·xH2O (1<x<4) (0.1 mol %) catalyzes the reaction of 2,2-dimethoxypropane with a series of substituted salicylaldehydes to generate the corresponding substituted 2,2-dihydro-1H-benzopyran (Formula 10)[8].