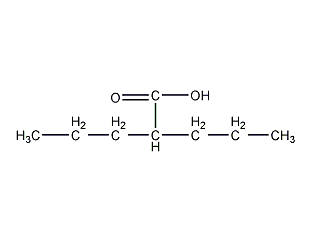
Structural formula
| Business number | 02GA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H16O2 |
| Molecular weight | 144.21 |
| label |
2-propylpentanoic acid, dipropylacetic acid, valproic acid, A-propyl valeric acid, di-n-propylacetic acid, 2,2-Di-n-propylacetic acid, 2-Propylpentanoic acid, Dipropylacetic acid, 4-Heptanecarboxylic acid, (CH3CH2CH2)2CHCOOH |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-66-1
MDL number:MFCD00002672
EINECS number:202-777-3
RTECS number:YV7875000
BRN number:1750447
PubChem number:24898751
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 0.904
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): Undetermined
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 221
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: 1.425
8. Flash point (ºC): 111
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 25ºC): Not determined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC) : Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined Determined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Very slightly soluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD5O: 670mg/kg
Mouse oral LD5O: 1098mg/kg
Guinea pig oral LD5O: 824mg/kg
p>
Ecological data
It is extremely harmful to water and toxic to fish. Do not let the product enter the water body.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.63
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 155.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 369.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 31.8
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.10
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 93.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidants and strong alkali.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from dipropylmalonic acid through elimination and decarboxylation. Put dipropylmalonic acid into the reaction pot and heat it to 180°C. The reactants gradually melt and release a large amount of carbon dioxide gas. After the elimination reaction is completed, distill under reduced pressure and collect the 112-114°C (0.93-1.06kPa) fraction, which is 2-propylpentanoic acid, with a yield of 86%.
2. Preparation method:
Dipropylmalonic acid (3): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer and reflux condenser, add dipropylmalonic acid Diethyl ester (2) 122g (0.5mol), ethanol 220mL, 4% potassium hydroxide 400g, stir and reflux for 4 hours. The ethanol was distilled off under reduced pressure. Cool to room temperature, slowly add concentrated hydrochloric acid, adjust to pH 1, and precipitate solid. Cool, filter, wash with water and dry to obtain 75.0g of yellow crystals of dipropylmalonic acid (3), yield 80%, mp. 155~158°C. 2-Propylvaleric acid (1): Add 75.0g (0.4mol) of dipropylmalonic acid (3) into the reaction bottle, slowly heat the oil bath to 180°C, the reactant gradually melts, and a large amount of carbon dioxide gas is released. , until no carbon dioxide gas escapes. Distill under reduced pressure and collect the fractions at 120~123℃/1.86kPa to obtain light yellow 2-n-propyl acid ① (1) 49.5, yield 86%, nD141.4252. Note: ① It can also be prepared by reacting ethyl acetoacetate with n-bromopropane and then performing alkaline hydrolysis. [1]
Purpose
Used as pharmaceutical intermediates and organic synthesis.


