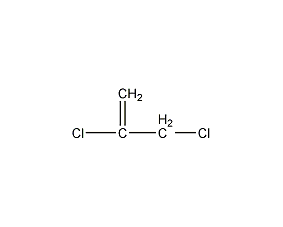
Structural formula
| Business number | 01NU |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H4Cl2 |
| Molecular weight | 110 |
| label |
2,3-Dichloropropene, 2,3-Dichloropropylene |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-88-6
MDL number:MFCD00000943
EINECS number:201-153-8
RTECS number:UC8400000
BRN number:1361491
PubChem number:24862352
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow liquid with a pungent odor similar to chloroform.
2. Density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 1.2150
3. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.1982
4 . Melting point (ºC): 10
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 94
6. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol– 1): -73.3
7. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4609
8. Flash point (ºC): 10
9. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4568
10. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1 ): 130.9
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in alcohol, soluble in ether, benzene and chloroform, insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity Rat LD50: 320mg/kg; Rat inhalation LC50: 500ppm/4H
Mouse inhalation LC50: 3100 mg/m3/2H
Rabbit Skin LD50: 1580 uL/kg
2. Neurotoxicity Rabbit skin test: 10mg/24H;
3. Teratogenicity Salmonella: 3ug/plate
E. coli: 625 ug/plate
Aspergillus: 225ppm
Hamster lung: 300 umol/L
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.21
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 95.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 213.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 24.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 9.99
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors���:0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 40.2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine Number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Number of stereocenters of uncertain chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Very flammable (fp 10 oC), toxic, should be handled in a fume hood.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, dry place. Store in a cool and ventilated warehouse.
Synthesis method
Prepared by refluxing 1,2,3-trichloropropane in water or ethanol solution and eliminating hydrogen chloride using NaOH.
Purpose
1. Used as raw material for plant growth regulator Aijiansu. Solvents, synthetic reagents, soil insecticide fumigants.
2.Alkylation 2,3-Dichloropropene is an ideal alkylating reagent and is often used for the addition of carbonyl enol anions. 2,3-Dichloropropene undergoes addition reactions with alcohols, amines, sulfones, ketimines and Schiff bases.
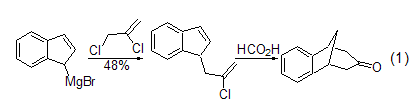
Grignard reaction The alkylation reaction between 2,3-dichloropropene and Grignard reagent[1]. In the synthesis of cyclic ketones, 97% formic acid can be used to cyclize the allyl side chains of alkenes (Formula 1)[2].
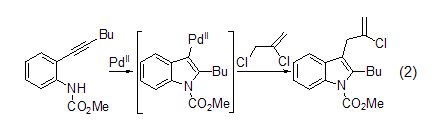
Palladium coupling reaction Under palladium catalysis, the cyclization reaction of alkynyl aniline and allyl chloride can produce 3-allyl indole (formula 2) in high yield[3]. There must be a proton-removing agent in the reaction mixture to prevent the organopalladium intermediate from being inhibited by H+.
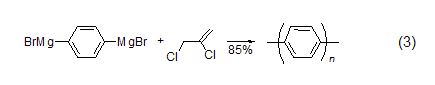
Aryl coupling reaction In the aryl Grignard reagent free radical coupling reaction, 2,3-dichloropropene is the electron acceptor. Polyparaphenylene (PPP) can be produced using 2,3-dichloropropene and a difunctional aryl Grignard reagent (Formula 3)[4].
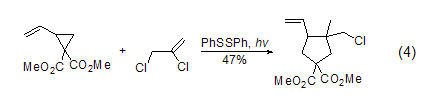
Free radical reaction Cyclopentane with functional groups can be prepared from vinylcyclopropane and trisubstituted propylene through photochemistry and DBU initiation (Formula 4)[5].
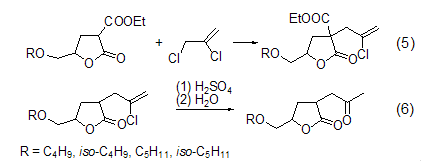
β-Chloroalkyl lactone can be obtained by alkylation reaction of 4-alkoxymethyl-2-ethoxycarbonylbutanol compound and 2,3-dichloropropene, followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation. The ester provides a new route for the synthesis of 2-acetonyl-4-alkoxymethylbutanol compounds (Formula 5, Formula 6)[6].