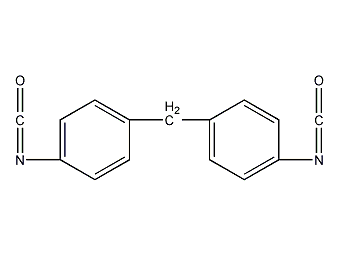
Structural formula
| Business number | 02KX |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C15H10N2O2 |
| Molecular weight | 250.25 |
| label |
Diphenylmethane-4,4’-diisocyanate, 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, Diphenylmethane 4,4′- diisocyanate, 4,4′ – diphenyl methane diisocyanate, Functional Materials, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:101-68-8
MDL number:MFCD00036131
EINECS number:202-966-0
RTECS number:NQ9350000
BRN number:797662
PubChem number:24860077
Physical property data
1. Character: White to light yellow molten solid, with pungent odor when heated.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.20
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 8.64
4. Melting point (ºC): 40-41
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 190
6. Boiling point (ºC, 4mmHg): 210
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
p>
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20.2ºC): Not determined
12. Saturated vapor Pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 0.07
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V /V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in acetone, benzene, kerosene, etc.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat inhalation LC50: 15ppm, oral administration within 2 hours – rat LD50: 9200 mg/kg; oral administration – mouse LD50: 2200 mg/kg
Ecological data
Water hazard class 1 (German Regulation) (self-assessment via list) The substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Do not allow undiluted or large amounts of product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 74.38
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 221.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 574.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 45.6
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10 -24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 29.49
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 5.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 58.9
7. Number of heavy atoms: 19
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 332
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants, acids, alcohols, and humid air. Soluble in acetone, carbon tetrachloride and other solvents. It is toxic, with lower vapor pressure than TDI, less irritating to respiratory organs, and irritating to skin, mucous membranes and eyes. It is easy to form dimers at room temperature and turn yellow in color. It is also easy to react with compounds containing head hydroxyl groups and amines. 2.Can cause moderate eye irritation and mildskin irritation, can cause skin allergies, the maximum allowed in the air The concentration is 0.02×10-6.
Due to the active chemical properties of MDI, avoid direct contact with the skin and splashing into the eyes during operation, and wear necessary protective equipment (gloves, protective glasses, work clothes, etc.).
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, alcohols, etc. and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills. The storage temperature should not exceed 20°C, and it should be strictly waterproof and moisture-proof, and avoid direct sunlight. 2.200L galvanized iron drum, 18L tinplate drum. When stored below 5°C, the container must be strictly dry and sealed and protected with dry nitrogen during storage. Once water leaks into the container, be sure not to seal it too tightly and leave a vent to prevent it from exploding.
Synthesis method
1. (1) Phosgene synthesis method Preparation of diaminodiphenylmethane from the condensation of aniline and formaldehyde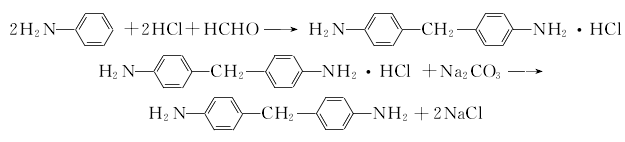 This product is obtained from the reaction of 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane and phosgene. The phosgenation reaction is carried out in a solvent. Hydrogen chloride is produced during the reaction, which is absorbed into hydrochloric acid. The crude product obtained by the reaction is distilled and refined to obtain the finished product.
This product is obtained from the reaction of 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane and phosgene. The phosgenation reaction is carried out in a solvent. Hydrogen chloride is produced during the reaction, which is absorbed into hydrochloric acid. The crude product obtained by the reaction is distilled and refined to obtain the finished product. 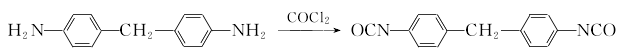 The production process of MDI has many similarities with products such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI). (2) Non-phosgene synthesis method: At room temperature, two drops are placed on a 1000ml three-neck bottle containing a solution of 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (29.7g, 0.15ml) in dichloromethane (300ml). Liquid funnel, which contains respectively bis(trichloromethane) carbonate (29.6g, 0.1ml) dichloromethane (200ml) solution and Na OH (24g, 06mol) aqueous solution (200ml), slowly add dropwise The aqueous solution of bis(trichloromethane) carbonate in dichloromethane and NaOH was added to the vigorously stirring 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane solution in dichloromethane. The reaction system was slightly heated. Control the dripping speed of the solution in the two solution funnels to maintain the pH value of the reaction system between 11 and 12 during the entire reaction. Immerse the reaction bottle in a cold water bath and keep the reaction system at about room temperature. After the solution is added dropwise, continue the reaction at room temperature for 2 hours. After the reaction, separate the aqueous layer and the methylene chloride layer in a separatory funnel. Extract the aqueous layer with 2×20 ml methylene chloride. Combine the organic layers, dry them with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and remove most of the solvent. The components are dissolved in silica gel. Use dichloromethane:light petroleum ether (7:3) as eluent for separation on column chromatography to obtain 28.45 g of light yellow product with a yield of 87% and a melting point of 40-42°C. 2. See the preparation of 1.5-naphthalene diisocyanate.
The production process of MDI has many similarities with products such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI). (2) Non-phosgene synthesis method: At room temperature, two drops are placed on a 1000ml three-neck bottle containing a solution of 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (29.7g, 0.15ml) in dichloromethane (300ml). Liquid funnel, which contains respectively bis(trichloromethane) carbonate (29.6g, 0.1ml) dichloromethane (200ml) solution and Na OH (24g, 06mol) aqueous solution (200ml), slowly add dropwise The aqueous solution of bis(trichloromethane) carbonate in dichloromethane and NaOH was added to the vigorously stirring 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane solution in dichloromethane. The reaction system was slightly heated. Control the dripping speed of the solution in the two solution funnels to maintain the pH value of the reaction system between 11 and 12 during the entire reaction. Immerse the reaction bottle in a cold water bath and keep the reaction system at about room temperature. After the solution is added dropwise, continue the reaction at room temperature for 2 hours. After the reaction, separate the aqueous layer and the methylene chloride layer in a separatory funnel. Extract the aqueous layer with 2×20 ml methylene chloride. Combine the organic layers, dry them with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and remove most of the solvent. The components are dissolved in silica gel. Use dichloromethane:light petroleum ether (7:3) as eluent for separation on column chromatography to obtain 28.45 g of light yellow product with a yield of 87% and a melting point of 40-42°C. 2. See the preparation of 1.5-naphthalene diisocyanate.
Purpose
Used as raw material for polyurethane foam, rubber, fiber, coatings, etc. is the main raw material for synthetic polyurethane adhesives and sealants. It is also used in the manufacture of polyurethane coatings, polyurethane foams, Rubber, catalysts, adhesives, herbicides, artificial leather, elastic fibers, synthetic leather, etc.


