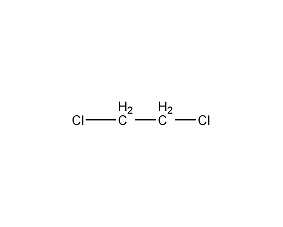
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UK |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H4Cl2 |
| Molecular weight | 98.96 |
| label |
Symmetric dichloroethane, Ethylene dichloride, 1,2-Dichloroethane, Ethylene dichloride, 1,2-Bichloroethane, Ethylene dichloride, Sym-Dichloroethane, Ethylene chloride, EDC; Brocide, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-06-2
MDL number:MFCD00000963
EINECS number:203-458-1
RTECS number:KI0525000
BRN number:605264
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: colorless or light yellow transparent liquid with an odor similar to chloroform. [1]
2. Melting point (ºC): -35.7[2]
3. Boiling point (ºC): 83.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.26[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.42[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 13.33 (29.4℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1243.9[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 290[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.36[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.48 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 13[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 413 [12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 16.0[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%) : 6.2[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in ethanol, ether, chloroform and most common solvents. [15]
16. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.440
17. Critical volume (cm 3·mol-1): 225
18. Critical compression factor: 0.259
19. Eccentricity factor: 0.288
20. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 7.814
21. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 253.6
22. Solubility parameter (J· cm-3)0.5:20.250
23.van der Waals area (cm2·mol– 1): 6.300×109
24. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 43.700
25. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -132.84
26. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 305.96
27. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1 ): -74.2
28. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 77.32 p>
29. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -167.99
30. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 208.53
31. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1 ): -82.42
32. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1The method is to chlorine ethylene and chlorine in 1,2-dichloroethane medium to generate crude dichloroethane and a small amount of polychlorides, add alkali to flash evaporate to remove acidic substances and some high boiling substances, and wash with water until neutral , azeotropic dehydration and distillation to obtain the finished product.
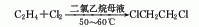
2. Ethylene oxychlorination method Ethylene is directly chlorinated with chlorine to form dichloroethane. The hydrogen chloride recovered from the cracking of dichloroethane to produce vinyl chloride, the oxygen-containing gas (air) and ethylene preheated to 150-200°C are passed through a copper chloride catalyst loaded on alumina at a pressure of 0.0683-0.1033MPa; React at a temperature of 200-250°C, and the crude product is cooled (condensing most of the trichloroacetaldehyde and part of the water); pressurized; refined to obtain the dichloroethane product.
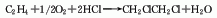
3. From petroleum cracked gas or Direct chlorination of ethylene in coke ovens. In addition, 1,2-dichloroethane is also a by-product in the production of chloroethanol and ethylene oxide.
4. Wash the industrial product 1,2-dichloroethane with concentrated sulfuric acid until the acid layer is colorless, then wash it with 5% calcium hydroxide solution, then wash it once with water, and remove the water. layer. After drying with anhydrous calcium chloride, perform distillation. 1,2-Dichloroethane can form an azeotropic mixture with water, containing 8.9% water and having an azeotropic point of 7.7°C. Utilize this characteristic to remove a large amount of water and then dry and distill it to obtain pure 1,2-dichloroethane.
5. Suspend the catalyst ferric chloride, copper chloride or antimony chloride in dichloroethane as the reaction medium, introduce the gases ethylene and chlorine respectively for reaction, and control the reaction temperature to 50 ~70℃, reaction pressure 0.4~0.5 MPa:
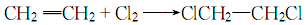
The product obtained by the reaction is washed with water to remove the hydrogen chloride and catalyst, left to stand for layering, and the water layer is separated. Then it is washed with 1% to 2% sodium hydroxide, and the water layer is separated, followed by azeotropic distillation and steamed out. The azeotrope is allowed to stand to separate the water layer, and after drying, it is then distilled to obtain pure 1,2-dichloroethane.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as raw materials for vinyl chloride; ethylene glycol; oxalic acid; ethylenediamine; tetraethyl lead; polyethylene polyamine and benzoyl. It is also used as a solvent for grease, resin, rubber, dry cleaning agent, pesticide preformin, caffeine, vitamins, hormone extractant, wetting agent, soaking agent, petroleum dewaxing, anti-seismic agent, and is also used in pesticide manufacturing and pharmaceuticals. Methionin; the raw material of piperazine. In agriculture, it can be used as food; grain fumigant; soil disinfectant, etc.
2. Used for boron analysis, oil and tobacco extraction agent. Also used in the manufacture of acetyl cellulose.
3. Used as analytical reagents, such as solvents and standard materials for chromatographic analysis. It is also used in the extraction of oils and in organic synthesis.
4. Used as detergent, extraction agent, pesticide and metal degreasing agent.
5. Used as a solvent for wax, fat, rubber, etc. and as a grain insecticide. [31]


