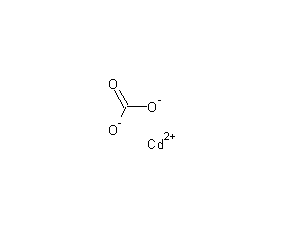
Structural formula
| Business number | 05AX |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CdCO3 |
| Molecular weight | 172.42 |
| label |
flux, catalyst, stabilizer, Plasticizer |
Numbering system
CAS number:513-78-0
MDL number:MFCD00010918
EINECS number:208-168-9
RTECS number:FF9320000
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24853282
Physical property data
1. Properties: Trigonal crystal system, white powder.
2. Density (g/ cm3, 25/4℃): 4.258
3. Relative steam density (g/cm3 , air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 500
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 8kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºF): Undetermined
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC) : Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14 . Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19 . Solubility: Insoluble in water and organic solvents, soluble in acid, potassium cyanide, and ammonium salts.
Toxicological data
1. Cadmium compounds with low solubility first act on the respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract. The absorption effects are manifested as damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system, internal organs, mainly the heart, kidney, liver, skeletal muscle and bone tissue. . Acute poisoning by cadmium oxide dust can cause irritation symptoms of the upper respiratory tract and deep respiratory mucosa, such as sweet taste in the mouth, forehead pain, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and upper abdominal pain. Symptoms of chronic poisoning are reduced sense of smell, headache, and weight loss.
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. TautovarianceNumber of solids: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 63.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 18.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. The number of uncertain stereocenters of atoms: 0
13. The number of determined stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. The number of uncertain stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
1. At 310℃, its color changes, from white to yellow, and then to brown. When burned to 500°C, CO2 is released and converted into cadmium oxide. Dry or wet cadmium carbonate is stable in the air and does not decompose when boiled in water for a long time. When irradiated with light with a wavelength of 300 to 400 nm, ultraviolet fluorescence occurs. It reacts with hydrogen at room temperature and is instantly reduced to metal. It reacts with liquid sulfur at 200~300℃ to generate cadmium sulfide and release sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide. Solubility: 2.8μg/100g H2O, soluble in acid, ammonia and cyanide solution, density: 4.25g/cm3, stable at room temperature.
2.Very poisonous! Cadmium compounds with low solubility first act on the respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract, and are absorbed into the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and internal organs. Mainly damage to heart, liver, kidney, skeletal muscle and bone tissue. Acute poisoning by cadmium dust can cause irritation symptoms of the upper respiratory tract and deep respiratory mucosa, such as sweet taste in the mouth, forehead pain, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and upper abdominal pain. For other poisoning symptoms, see Cadmium Oxide. p>
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse.
2. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. The packaging is sealed.
3. They should be stored separately from acids and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Cadmium nitrate method: Cadmium ingot reacts with nitric acid to generate cadmium nitrate, and then reacts with soda ash to generate cadmium carbonate. It is then washed, dried and crushed to obtain the finished cadmium carbonate. Its response equations:

2. Hydrochloric acid method: melt the cadmium ingot, pour it into water and crush it into granules, add hydrochloric acid to dissolve it to form cadmium chloride, and at the same time Add a small amount of nitric acid, add ammonia under stirring to adjust the pH to 5~6, then add a small amount of hydrogen peroxide to remove iron, filter it and react with the prepared soda ash solution to pH 9~10, rinse with water until neutral, then filter and dry at 120°C , to obtain finished cadmium carbonate products. Its reaction equation:
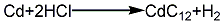
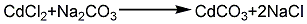 3. Weigh 18g CdCl2 and dissolve it in 50mL water. Then weigh 10g ammonium carbonate and dissolve it in 50mL water. Add the ammonium carbonate solution to the CdCl2 In the solution, after the precipitate is formed, drop in ammonia water to dissolve the formed precipitate. Transfer the solution to a fume hood and heat it in a water bath until the ammonia in the solution volatilizes and crystals settle down.
3. Weigh 18g CdCl2 and dissolve it in 50mL water. Then weigh 10g ammonium carbonate and dissolve it in 50mL water. Add the ammonium carbonate solution to the CdCl2 In the solution, after the precipitate is formed, drop in ammonia water to dissolve the formed precipitate. Transfer the solution to a fume hood and heat it in a water bath until the ammonia in the solution volatilizes and crystals settle down.
4.There are mainly two methods for industrial production of cadmium carbonate. Metathesis method: obtained by metathesis of alkali metal carbonates and chromium salts such as cadmium chloride or cadmium sulfate. The source of chromium is mostly metal cadmium as raw material, and can also be used as a by-product of zinc smelting and zinc barium white production. Carbonization method is obtained by absorbing carbon dioxide with cadmium hydroxide. 5.Heat 20% cadmium sulfate aqueous solution to boiling, slowly add 45~ while stirring Use about 20% ammonium carbonate aqueous solution at 50℃ to react with a pH value between 7.5 and 8:Let it stand until the precipitation is complete, filter it, and wash the precipitation several times with 30 to 40 times the volume of hot distilled water. After suction filtration, dry at 120~150℃ for 3 hours to obtain the reagent cadmium carbonate. The preparation of high-purity cadmium carbonate is also carried out according to this principle. The reagents used are high-purity cadmium sulfate, high-purity ammonium carbonate and conductive water.
Purpose
1. Intermediates and insulating materials used in the manufacture of polyester. It is used as a flux for glass pigments, a catalyst for organic reactions, a plasticizer and stabilizer for plastics, and as a raw material for the production of cadmium salts.
2.As an intermediate for manufacturing polyester and a co-solvent for glass pigments, it can be used to make optical glass and be used as insulating materials , catalysts for organic reactions, plasticizers and stabilizers for plastic paper, and raw materials for the production of chromium salts.
3.In surface treatment, prepare soluble cadmium salts for adding cadmium to cadmium electroplating or cadmium alloy electroplating solutions.


