Background and overview[1]
Diphenyl ether contact herbicide, chemical name: 2,4-dichlorophenyl-4′-nitrophenyl ether. The original drug is a light yellow needle-shaped crystalline solid, almost insoluble in water, and easily soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetic acid, acetone and benzene. Stable in air. It mainly uses position difference to select weeding. The pesticide forms a drug layer on the surface of the soil. When the weeds germinate, the germs contact the drug through the drug layer and are poisoned. Herbicides only work under the influence of light and are inactive in the dark. In plants, it interferes with plant respiration and inhibits ATP production. Herbicidal activity is temperature-related and is poor below 20°C. It is suitable for rice, cotton, peanuts, wheat, barley, vegetables, fruit, mulberry and tea gardens to control annual grass weeds and broadleaf weeds.
Structural formula
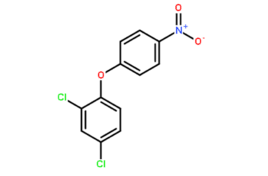
Apply[2]
The dosage form of herbicide is 25% wettable powder and 40% and 50% powder. It is used for weeding in rice fields, has good effects, and is suitable for a variety of soil types and temperatures. It is easily adsorbed by soil and has little ability to spread downward or around. It can maintain its efficacy on topsoil for 20 to 30 days. Herbicide is a contact herbicide that can only produce toxicity when exposed to light. Its efficacy is not high when the temperature is below 20°C; when it is above 25°C and exposed to sunlight, its efficacy increases significantly. Herbicidal ether is a broad-spectrum herbicide that can control barnyard grass, three-edge grass, knotweed, etc. in rice fields. It can also be used for weeding in dry lands such as cotton, peanuts, sugar cane, rape, and mulberry fields.
Key points in poisoning diagnosis[3]
1. Poisoning symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia, cyanosis and jaundice.
2. Liver and kidney function damage.
Processing principles[3]
1. For oral poisoning, induce vomiting, gastric lavage, and catharsis.
2. Patients with cyanosis should be treated with methylene blue. Add 20-40ml of 25% glucose solution at 1-2 mg/kg and inject slowly intravenously. It can be reused if necessary.
3. For patients with hemolytic anemia, use adequate amounts of adrenocortical hormone as soon as possible. Sodium bicarbonate is taken orally to alkalinize the urine and prevent hemoglobin from accumulating in the urine.
4. Pay attention to the prevention and treatment of liver and kidney failure.
5. Symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Main reference materials
[1] Agricultural Dictionary
[2] Encyclopedia of Chinese Adult Education·Chemistry·Chemical Engineering
[3] Practical Poisoning First Aid Digital Manual


