Background and overview[1][2]
2-Chlorophenol is an important organic chemical raw material. 2-Chlorophenol can be used in medicines, pesticides, dyes and other organic synthesis raw materials. 2-Chlorophenol can be phosgenated to obtain ortho-chlorophenyl chloroformate, which is an amino acid. It is an intermediate of the formate ester pesticide pyroprofen, and 2-chlorophenol is also an intermediate of the pesticide profenofos.
2-Chlorophenol is a typical phenol pollutant. 2-Chlorophenol is a colorless liquid with an odor, easily soluble in water, and also soluble in organic solvents such as hexanol and hydrochloric acid. It is an intermediate in the industrial production of pesticides, medicines, and dyes. 2-Chlorophenol is flammable and can produce harmful gases such as carbon monoxide and ammonia chloride. It is also toxic (low toxicity) and can be absorbed through the skin. Long-term excessive exposure can cause insomnia, fatigue, headaches, etc., seriously affecting human health.
Chlorophenolic organic compounds can be obtained by direct chlorination of phenolic compounds or hydrolysis of chlorobenzene. They are a typical type of organic pollutants that are difficult to degrade. Due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial, bactericidal and insecticidal effects, it is widely used in dyes, papermaking, preservatives, herbicides, fungicides and other industries. In addition, chlorophenols by-products may also be produced during waste incineration, chlorine bleaching of pulp, and chlorination and disinfection of drinking water.
Physical and chemical properties and structure[1]
The molecular formula of 2-chlorophenol is C6H5ClO, also known as o-chlorophenol. It is a colorless liquid with an odor, easily soluble in water, and also soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. 2-Chlorophenol is flammable and can produce harmful gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride. It is also toxic and can be absorbed through the skin and be harmful to the body. Generally used as raw materials for medicine, pesticides, dyes and other organic synthesis. The melting point is 7℃, it is volatile and has an unpleasant odor. The boiling point is 174.5℃ and the flash point is 63.9℃. It is obtained by oxidizing phenol into ortho- and para-isomers and then separating them. It can also be obtained by chlorination and acidification of sodium phenolate, and can evaporate together with steam.
Phenolic compounds are highly toxic and difficult to degrade. The U.S. EPA regards them as priority pollutants. Phenolic compounds are a kind of cell protoplasm poison. Their toxic effect is a chemical reaction with proteins in the cell protoplasm to form Denatured proteins make cells inactive. The pathological changes caused mainly depend on the concentration of the poison. Low concentrations can denature cells, and high concentrations can cause protein coagulation. Although low concentrations are not as serious as high concentrations in local damage, low concentrations Due to its strong penetrating power, it can penetrate into deep tissues, so the consequences are more serious, with varying degrees of dizziness, headaches, rashes, skin itching and various neurological symptoms. 2-Chlorophenol is flammable when exposed to open flames and high heat. Decomposed by high heat to produce toxic and corrosive fumes. The combustion products are carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen chloride.
Preparation[2]
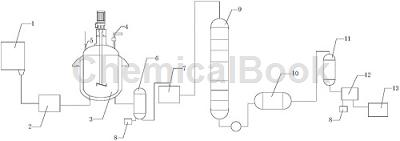
The production device includes a storage tank 1, a reaction device, a waste gas absorption device 8, a fractionation device and a purification device. The storage tank 1 is connected to the reaction device. The reaction device includes a phenol preheater 2, a reaction kettle 3, and chlorine gas. Inlet pipe 4, thermometer 5, steam tank 6 and crude product tank 7. One side of the bottom end of storage tank 1 is connected to the feed port of phenol preheater 2 through a conveyor pipe, and the outlet of phenol preheater 2 is connected through a conveyor The pipe is connected to the feed port of the reaction kettle 3. One side of the upper end of the reaction kettle 3 is provided with a thermometer 5. One end of the thermometer 5 is located inside the reaction kettle 3. The other side of the upper end of the reaction kettle 3 is provided with a chlorine gas introduction pipe 4. , the discharge port of the reaction kettle 3 is connected to the feed port of the steam tank 6 through a conveying pipe. The bottom end of the steam tank 6 is provided with two discharge ports, one of which is connected to the exhaust gas absorption device 8, and the other is connected to the waste gas absorption device 8. One outlet is connected with the feed port of the crude product tank 7 .
The fractionation device includes a rectification tower 9 and a condenser 10. The feed port of the rectification tower 9 is connected to the outlet of the crude product tank 7. The outlet of the rectification tower 9 is connected to the outlet of the condenser 10 through a conveying pipe. The feed port is connected; the purification device includes a crystallizer 11, a fine product tank 12 and a receiving tank 13. The feed port of the crystallizer 11 is connected to the outlet of the condenser 10, and the outlet of the crystallizer 11 is connected to the outlet of the condenser 10. The feed port of the fine product tank 12 is connected, and the bottom end of the fine product tank 12 is provided with two discharge ports, one of which is connected to the receiving tank 13, and the other discharge port is connected to the waste gas absorption device 8;
An anti-corrosion coating is also provided on the inner wall of the reactor 3. The anti-corrosion coating is formed by coating the inner wall of the reactor 3 with anti-corrosion coating. The anti-corrosion coating is composed of two components, A and B. According to the mass ratio, A:B =1:2; Component A includes the following components by mass parts: silicone modified epoxy resin: 25 parts, pigment: 11 parts, filler: 12 parts, dispersant: 9 parts, film-forming aid : 9 parts, defoaming agent: 11 parts; component B includes the following components by mass parts: polyphenylene ether resin powder: 18 parts, toluene: 8 parts, plasticizer: 5 parts, coupling agent: 8 parts, flame retardant: 2 parts, composite rare earth: 18 parts; among them, the pigment is one of titanium dioxide, carbon black, barium sulfate or chromium oxide green.
The filler is one of glass flakes or alumina, the dispersant is one of sodium tetrapolyphosphate or sodium hexametaphosphate, and the film-forming assistant is one of ethylene glycol ether, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. , the defoaming agent is silicone; the plasticizer is one of dioctyl phthalate or dibutyl phthalate, and the coupling agent is at least one of silane coupling agent or zirconium coupling agent. The flame retardant is phosphate tryster. The composite rare earth includes the following components in terms of mass percentage: dysprosium: 15%, cerium: 22%, praseodymium: 4%, neodymium: 2%, the rest is lanthanum element, the above lanthanumThe sum of the rare earth components is 100%.
The storage tank 1 and the receiving tank 13 are provided with temperature sensors, the conveying pipe connecting the distillation tower 9 and the condenser 10 is provided with a metering device, and the phenol preheater 2 is provided with a heating tank. There is a heating tube installed in the reactor, which is isolated from the phenol barrel by a support plate. The reactor 3 is equipped with a stirrer, which is a double-spiral stirrer. The inlet end of the chlorine gas introduction pipe 4 and the outlet end of the waste gas absorption device 8 Valves are provided respectively; it also includes a production process of high-purity o-chlorophenol, and the production process steps are as follows:
(1) Pour the phenol in the storage tank into the phenol preheater through the delivery pipe, open the steam valve to heat the phenol into a liquid state;
(2) The generated liquid phenol flows into the reaction kettle, add 2-chlorophenol, solvent and catalyst, then stir for 20 minutes, and gradually heat to 66°C, open the chlorine gas inlet pipe valve and introduce chlorine gas into the reaction kettle, control The chlorine gas feed rate is 15g/h so that the chlorine gas is added within 3 hours. Keep the temperature inside the reactor at 150°C and continue stirring for 15 minutes to obtain mixed phenol;
Among them, based on the material ratio, 2-chlorophenol: chlorine: catalyst = 1:1.6:0.005;
(3) After the mixed phenol enters the steam tank, it gradually heats up. After the temperature rises, it is driven to the crude product tank and then distilled. The distillation stops after the distillation temperature reaches 175°C;
(4) The distillation residue in step (3) is cooled to room temperature and then flows into a crystallizer, filtered, and dried to obtain high-purity o-chlorophenol crystals.
Main reference materials
[1]Hu Xiaomin, Dong Yihua, Li Liang, Lu Juan, He Yingdian, & Gao Yang. (2010). Study on the degradation characteristics of 2-chlorophenol by photosynthetic bacterium psb-1d. Environmental Science, 31(7), 1672 -1678.
[2] Qu Jiuhui, Lin Su, Tian Baozhen, Liu Huijuan, & Lei Pengju. (2001). Research on the removal of o-chlorophenol in drinking water by high-iron oxidation. Journal of Environmental Science, 21(6), 701-704 .
[3] Tang Jierong. A production device for high-purity o-chlorophenol.


