Background and overview[1][2]
Diphenylcarbazone (DPC) is an important organic analytical reagent. It can form blue, purple, and red chelates with many heavy metal ions, so it is widely used to determine heavy metal ions such as Cr (IV), Chromogenic reagents or photometric reagents for Hg (II), Mo(VI), Cu(II), etc. Because the chromogenic system of diphenylcarbazone has the advantages of high sensitivity, good reproducibility, and accuracy, it is still an important analytical reagent for detecting trace metal ions in the fields of analytical chemistry, petrochemical industry, and environmental protection. It has broad application prospects. Diphenylcarbazone (DPC) is usually produced by oxidative dehydrogenation of diphenylcarbazone. There are two main methods reported in the literature, using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant in an alkaline medium, or using potassium chlorate in an acidic medium. However, the operation is cumbersome and the yield is low. Another method is to use ferric chloride as the oxidant to perform unilateral dehydrogenation of diphenylcarbohydrazine under stirring at room temperature, and synthesize diphenylcarbohydrazone simply and efficiently with good yield. Reaching 92%, this method has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials, simple operation, mild conditions, and easy separation and purification of the product.
Apply[2-5]
Diphenylcarbazone is mainly used as analytical reagent, chromatographic analysis reagent, adsorption indicator and complex indicator for the determination of cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, mercury, molybdenum, lead and zinc. Examples of its application are as follows:
1. Detect trace chloride ions in boiler water. The test method is: in an aqueous solution with a pH of 2.3-3.2, chloride ions (Cl-) react with mercury ions (Hg2+) to generate slightly dissociated mercury chloride that is soluble in water. Within the range of pH 2.8-3.2, Diphenylcarbahydrazone [diphenylazocarbonylhydrazide (C13H12ON4)] and excess mercury ions can form a purple complex. Use a luminescence photometer to measure the absorbance of the purple complex and compare it with the working curve to determine the chloride ions in the tested solution ( Cl-) content.
2. Detect trace chloride ions in limestone slurry. Chloride ions react with the mercury ions in mercury nitrate to form slightly soluble mercury chloride. At the end of the titration, the excess mercury ions react with the diphenylcarbazone indicator to form a purple complex, and the color of the solution changes from yellow to green. The purple color is the end point, and the chloride ion content is finally calculated based on the titration of mercury nitrate. The method is simple to operate and low in cost, and a conventional buret can be used to complete the experiment; the interference of sulfite is eliminated, the precision is high, and several ppm of chloride ions can be detected; the titration end point changes color obviously and is easy to identify.
3. Prepare zinc ion detection test paper. Zinc is a kind of trace element. The content in the human body and the daily intake required are very small, but it can play a decisive role in the development of the body. However, excessive zinc can cause great harm to the human body, and when zinc is enriched in the soil, it will also be enriched in plants, causing harm to people and animals who eat the plants. Irrigating farmland with zinc-containing sewage has a greater impact on crops, especially wheat. It will cause uneven emergence of wheat, few tillers, short plants, and chlorosis of leaves. Excessive zinc will also make the soil inactive, reduce the number of bacteria, and weaken the microbial effects in the soil. my country stipulates that the zinc content of domestic drinking water shall not exceed 1.0 mg/L, and the maximum emission concentration of zinc and its compounds in industrial wastewater is 5.0 mg/L. Therefore, zinc ion content detection is of great significance in industrial production, environmental testing, agricultural applications, food safety and other fields. The current detection methods for zinc content include atomic absorption spectrophotometry, dithizone extraction, etc. These detection methods not only require laboratory conditions, but also have complex operations, long detection times, and high costs, which are not conducive to rapid on-site detection. . Some research provides a new zinc ion detection test paper and its preparation method and application. The test paper is simple to make, low cost, easy to carry, and can quickly and conveniently detect zinc ion concentration on site. It specifically includes chromogenic test paper pieces. The chromogenic test paper pieces are prepared by soaking filter paper in an impregnation liquid, taking it out and drying it. The impregnation liquid is composed of diphenylcarbazone, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, ethanol, sodium thiosulfate, and distilled water. . The above-mentioned test paper is simple to make, low in cost, easy to use, does not pollute the environment, is environmentally friendly, does not require professional operation, and is especially suitable for rapid on-site detection of zinc content.
4. Rapidly characterize hexavalent chromium in jewelry. Chromium is widely distributed in nature and living organisms, mainly in the form of trivalent chromium and hexavalent chromium. Trivalent chromium is an essential trace element for the human body, and the toxicity of the accumulated amount needs to be further confirmed; hexavalent chromium is clearly toxic and harmful, and has the effect of causing cancer and inducing genetic mutations. Currently, it is widely concerned by the public due to environmental pollution and RoHS aspects. The detection of hexavalent chromium is currently widely used in the environment, food and other fields, but in the field of jewelry testing, it started late. In 2003, the European Union promulgated the RoHS Directive (2002/95/EC), which strictly restricted the use of six specific hazardous chemicals (including hexavalent chromium) in electronic and electrical products. Immediately, various countries responded and passed relevant bills to make this The scope of the directive extends to all types of materials and products, including the jewelry industry. Some studies have developed a qualitative method for rapid determination of hexavalent chromium in jewelry, which includes the following steps: using diphenylcarbazide as an indicator of hexavalent chromium. If the surface of the jewelry contains hexavalent chromium, react with 1 under acidic conditions. 5-Diphenylcarbazide reaction, in which hexavalent chromium is reduced to trivalent chromium, and diphenylcarbazide is oxidized to diphenylcarbhydrazone, and trivalent chromium further reacts with diphenylcarbhydrazone.��Generates a red-violet complex, and determines whether there is hexavalent chromium in the jewelry by observing whether there is color generation. This method can quickly make qualitative judgments and save a lot of time in detection.
Preparation [1][6]
Method 1: Take 0.242g (1mmol) diphenylcarbazide and 5mL acetone, add them to a 50mL two-neck flask equipped with a stirring device, heat them slightly and stir them to completely dissolve them, then add 0.54g (2mmol) FeCl 3· When 6H2O is dissolved in 5mL2N H2SO4, the color immediately changes to deep red. Stir for 15 minutes at room temperature. If a flocculent precipitate appears, add 15 mL of cold distilled water at a time and let stand in a cold water bath to allow the precipitate to precipitate completely. Filter, wash with a small amount of ether 2 to 3 times, and dry under vacuum at 50°C to obtain orange-red needle-like crystals. , yield 92%, melting point 154~156℃
![]()
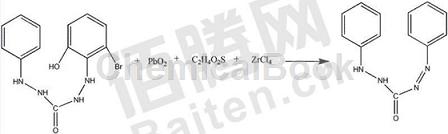
Method 2: The synthesis method of diphenylcarbahydrazone does not require the use of phenylhydrazine and hydrogen peroxide as reactants, which avoids the strong toxicity of phenylhydrazine and the greater harm to the health of synthesis operators, and reduces the cost of subsequent pollutant treatment. It is beneficial to reduce project costs. It also avoids the strong corrosiveness of hydrogen peroxide and reduces the requirements for corrosion resistance of equipment. It also avoids the disadvantages of poor stability of hydrogen peroxide and is not conducive to long-term storage. The intermediate links of the reaction are reduced a lot, and the reaction time It is also shortened a lot and the reaction yield is also improved. Specifically, it includes the following steps:
A: Add 1-phenyl-5-(2-hydroxy-6-bromophenyl)-carbazine and carbon tetrachloride solution to the reaction vessel, raise the solution temperature to 40-47°C, and add Lead oxide, control the stirring speed to 130-170rpm, react for 2-3h;
B: Layer the solution into layers, add zirconium tetrachloride powder, thioglycolic acid solution, and potassium chloride solution, control the temperature to 20-27°C, add propylamine solution and wash several times, and phenylacetonitrile solution and wash several times. Recrystallize from propylene glycol monobutyl ether solution and dehydrate with dehydrating agent to obtain the finished product diphenylcarbahydrazone.
Main reference materials
[1] A simple and effective new method for the synthesis of diphenylcarbazone
[2] CN201210036058.2 Test method for trace chloride ions in boiler water
[3] CN200610095319.2 Method for measuring chloride ions in limestone slurry by mercury nitrate titration
[4] CN201510035183.5 A zinc ion detection test paper and its preparation method and application
[5] CN201810696168.9 A qualitative method for rapid determination of hexavalent chromium in jewelry
[6] CN201710715100.6 Synthesis method of organic analysis reagent diphenylcarbazone


