Background and overview[1][2]
Chlorobenzene, also known as chlorobenzene, is a colorless and transparent liquid. Volatile. It has the smell of benzene and slight anesthetic properties. This product can form an explosive mixture with air, with an explosion limit of 1.83% to 9.23% (volume fraction). The chlorine atoms in this product can be hydrolyzed to produce phenol. If hydrolyzed in an ammonia solution, aniline can be produced. It can also be further chlorinated to produce polychlorinated benzene. It can be nitrated and sulfonated to generate nitrochlorobenzene and chlorobenzenesulfonic acid. This product is explosive and toxic. Inhaling its vapor can cause acute poisoning, headache, asthma, and further loss of consciousness. Contact with the skin can cause dermatitis. Rat oral LD502910mg/kg. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 75×10-6. Chlorobenzene was once mass-produced as a raw material for chlorine-based pesticides including DDT. Later, the use of these pesticides was restricted, and the demand also decreased. However, most of the current pesticides such as herbicides are aromatic halogen-containing compounds, and chlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene are their starting materials. Paradichlorobenzene has long been used as a household insecticide. Chlorobenzene, o-dichlorobenzene, and trichlorobenzene have strong dissolving power for organic compounds, so they are also commonly used as solvents.
Apply[2-4]
Chlorobenzene can be used as a raw material for the manufacture of o-nitrochlorobenzene, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene, p-nitrochlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, o-dichlorobenzene, phenol, aniline, etc. , the above compounds can be used in pigments, dyes, medicines, and rubber additives; they are also used as raw materials for the pesticide DDT; they can be used as heat transfer media in engineering; ethyl cellulose and resin solvents. Chlorobenzene compounds mainly include: chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, trichlorobenzene, tetrachlorobenzene, pentachlorobenzene and hexachlorobenzene. Chlorobenzene compounds are non-natural compounds with stable physical and chemical properties and are not easily decomposed. Chlorobenzene compounds are mainly used in the production industry of pesticides, dyes, medicines, plastics and daily chemical products. They can also be used for termite control, degreasing solvents, lubricant additives, functional additives for special engineering plastics, etc. The most commonly used ones are dichlorobenzene and trichlorobenzene. Among the isomers of dichlorobenzene, p-dichlorobenzene and o-dichlorobenzene are particularly important. Para-dichlorobenzene is widely used in the production of pesticides, dyes, medicines, plastics and daily chemical products, and can also be used as special purpose solvents, anti-rust agents, etc.; trichlorobenzene, as a non-flammable solvent, is used as a dye in the textile industry Carriers can also be used to synthesize a variety of important pesticides, medicines and dyes.
Examples of its application are as follows: preparation of nitrochlorobenzene. Nitration of chlorobenzene is an important chemical industrial reaction. Its nitration product, mononitrochlorobenzene, is mainly used as an intermediate for the synthesis of dyes, pesticides, medicines, developers, rubber antioxidants, etc. It is also a good high-boiling point solvent and moderate organic oxidant. , plays an important role in industrial production. Many derivatives of mononitrochlorobenzene also have broad market prospects.
Use a microchannel reactor to carry out chlorobenzene nitration reaction. This method uses nitric acid, sulfuric acid, water, and chlorobenzene as starting reaction raw materials. The mixed acid configuration, mixed acid and chlorobenzene preheating, and mixed acid are completed in the microchannel reactor system. Reaction with chlorobenzene and other processes. Nitric and sulfur mixed acid is used as the nitrating agent in the reaction. The effective concentration of sulfuric acid in the mixed acid is 50%~90%. The molar ratio of nitric acid and sulfuric acid in the mixed acid is 1:1~1:10. Chlorobenzene and nitric acid The molar ratio is 1:1.0~1:2.0, the reaction temperature is 50~100℃, and the reaction time is 30s~120s. The conversion rate of chlorobenzene can reach 97%, the selectivity of its product mononitrochlorobenzene is greater than 96.5%, and the ratio of ortho-para-nitrochlorobenzene is greater than 0.6. The enhanced mixed microchannel reactor used is particularly suitable for continuous nitrification reactions and has the characteristics of stable temperature control and process safety.
In addition, there is also research on using nitrogen dioxide to nitrate chlorobenzene to prepare p-nitrochlorobenzene. Chlorobenzene is reacted with nitrogen dioxide in a catalyst and oxygen atmosphere to prepare p-nitrochlorobenzene, which includes the following steps:
1) Stir chlorobenzene, catalyst and molecular sieve until evenly mixed;
2) After introducing nitrogen dioxide and protective gas, stir and react for 12-48 hours to obtain the crude reaction product;
3) Filter the crude reaction product to remove the catalyst and molecular sieves, let it stand to separate the organic phase, wash it with sodium bicarbonate solution and distilled water several times until the organic phase becomes neutral, and separate nitrochlorobenzene by distillation under reduced pressure. ;
4) After drying the nitrochlorobenzene, perform high-performance liquid chromatography analysis using nitrobenzene as the internal standard, and use the internal standard method to calculate the content of the nitration product components of chlorobenzene.
Preparation [1,5]
Method 1: Under the action of iron catalyst, benzene is chlorinated. During the reaction process, in addition to chlorobenzene [1], dichlorobenzene is also generated at the same time. Because the density of chlorobenzene is smaller than that of dichlorobenzene, and The amount of production is large, so gravity can be used to separate it, and then the separated crude chlorobenzene can be distilled and refined. The reaction can be carried out in the gas phase, and the reaction temperature is 400~500℃. It can also be carried out in the liquid phase. The reaction temperature is 40~60℃. Chlorine gas is slowly passed into benzene, reacted under the action of a catalyst, and unreacted chlorine gas is recovered.
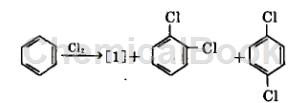
Method 2: A method for preparing chlorobenzene, p-dichlorobenzene and o-dichlorobenzene during the chlorination of benzene. The method includes continuously flowing into an external loop reactor containing high activity and high p-dichlorobenzene selection. The dry benzene and chlorine gas of the catalyst must have sufficient residence time, and the benzene and chlorine gas must be reacted at the set reaction temperature to produce p-dichlorobenzene, ortho-dichlorobenzene, and co-produced monochlorbenzene; Among them: the external loop reactor aspect ratio = H/D is generally 10-30, preferably 20; the pipe diameter ratio = D/d is generally 1.5-0.5, preferably 1.0.
The residence time of benzene in the reactor is generally 0.5-1.5h, preferably 0.8-1.2h, and preferably 1.0h; the amount of benzene introduced per cubic meter of volume of the loop reactor is: The gas riser can reach a maximum of 2.0 tons/hour, preferably 1.5 tons/hour, and preferably 0.8 tons/hour; the amount of chlorine gas introduced should be 250m3/h (11.20kmole)-650m3/h (29.07kmole) Among them; catalysts with high activity and high selectivity for dichlorobenzene include but are not limited to antimony pentasulfide, antimony trisulfide, iron trisulfide, iron trichloride + S, pyrite + S, the latter two The ratio of sulfur addition should meet the molar ratio of iron to sulfur of 2:3; the catalyst used should be crushed to less than 10 microns, preferably less than 5 microns, and preferably less than 2 microns; the amount of catalyst should be 0.06 (W/%) of the amount of benzene added )-0.1(W/%); the reaction temperature should be between 40℃-50℃;
Main reference materials
[1] Practical Fine Chemical Dictionary
[2] CN201110346793.9 A method for chlorophenyl nitro reaction using microchannel reactor
[3] CN201210475672.9 Method for preparing p-nitrochlorobenzene by nitrating chlorobenzene with nitrogen dioxide
[4] Wang Shuo, Dai Bingye, Zhang Yan. Research status of determination methods of chlorobenzene compounds[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2008, 23(1): 83-86.
[5] CN201410048269.7 Method for preparing chlorobenzene, p-dichlorobenzene and o-dichlorobenzene during chlorination of benzene


