Background and overview[1][2]
P-isopropyltoluene (commonly known as p-cymene) is a very important chemical product and a widely used organic synthesis intermediate. As the market demand for p-cresol, especially high-purity p-cresol, continues to grow in recent years, it can be expected that the main use of p-cymene will be to synthesize p-cresol, and this research field has therefore been widely used. Background, contains huge market potential. Traditionally, cumene (i.e. cymene) is produced by the Frield-Crafts alkylation reaction of toluene and propylene (or propanol). This is a reaction with poor selectivity. What is actually obtained is a mixture of o-, m- and p-cymene, and the cresol produced from it is also a mixed cresol. In recent years, there have been continuous reports of highly selective synthesis of p-cymene, and the prepared p-cumylene can be used to synthesize high-purity p-cresol. The synthesis method of cumene can be summarized into two routes from the material point of view. One is to use toluene as the raw material (i.e., isopropylation of toluene), and the second is to use turpentine as the raw material (i.e., the isomerization of terpenes in turpentine). chemical and dehydrogenation reactions).
Apply[1-3]
P-isopropyltoluene (commonly known as p-cymene) is a very important chemical product and a widely used organic synthesis intermediate. It can be used in soft drinks, iced foods, candies, chewing gum, and seasonings; also It can be used to synthesize a variety of polycyclic musk-type spices such as parasol musk, sandalwood musk, tona musk, etc., drugs, herbicides, fungicides, etc.; terephthalic acid made from it can be used to make synthetic resins and synthetic fibers. and plasticizer; p-cymene is oxidized and acidolyzed to obtain p-cresol and the co-product acetone, and p-cresol is an important raw material for the synthesis of pesticides, medicines, synthetic materials, spices and other fine chemical products. Examples of its application are as follows:
1. Synthetic musk. Tonalide is a synthetic musk with a tetraline structure. It has excellent fragrance, elegant aroma, long-lasting fragrance, acid and alkali resistance, does not change color under natural light, has strong diffusion power, and is not irritating to human skin. It blends well with other spices and is an ideal fragrance raw material. It is widely used in cosmetics, perfumes, tobacco, flavors and medicines, and has become one of the most promising synthetic musk products. The synthesis method uses cumene as raw material, cyclizes it with olefins under the catalysis of mixed Lewis acid, and then undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction in an ether solvent to obtain a purity of ≥98% with a total yield of close to 85%. Breathe in the musk. The selectivity and yield of cyclization were improved by improving the catalyst composition, and the conditions of Friedel-Crafts reaction were optimized by screening solvents. Compared with the existing technology, this method has the characteristics of mild conditions, simple operation, and high purity and yield of the product obtained.
2. Method for preparing hexamethyltetralin. Hexamethyltetralin is 1,1,3,4,4,6-hexamethyl-1,2,3,4-tetralin, or HMT for short. , is an important intermediate for the synthesis of Tuna Musk fragrance. Tuna Musk is a kind of musk fragrance with strong musk aroma, long-lasting fragrance and strong aroma diffusion ability. In addition, it is acid and alkali resistant and has good light stability. It is non-irritating to human skin and blends well with other fragrances. It is an ideal synthetic musk product with great development potential and has been widely used in perfumes, cosmetics and detergent fragrance formulas. The preparation method is as follows: using an acidic room temperature ionic liquid as a catalyst, cyclic hydrocarbons as solvents, p-isopropyltoluene and olefins as raw materials, and performing an alkylation reaction in the presence of a hydrogen transfer reagent; the acidic room temperature ionic liquid catalyst is a metal halide. It is prepared by reacting with alkyl-containing pyridine amine halide, alkyl-containing amine hydrohalide or alkyl-containing imidazole amine halide. The above-mentioned process is simple, has high product selectivity, and a relatively considerable yield. The ionic liquid catalyst used in the reaction is easy to separate from the reaction liquid and can be recycled. The process does not produce three industrial wastes and is a green and environmentally friendly process. Craftsmanship.
Preparation [1]
1. Use toluene as raw material to synthesize p-isopropyltoluene
So far, this synthesis route is mostly used in industry to produce cumene. It is realized by Frield-Crafts alkylation reaction of toluene and propylene (or isopropyl alcohol), usually using AlCl3 as catalyst. Due to the weak ortho- and para-positioning effect of the methyl group in the toluene molecule and the reversibility of the reaction, as well as the relative thermodynamic stability of meta-alkylbenzene compared with ortho- and para-alkylbenzenes, the reaction product contains only p-isopropyl In addition to methyl toluene and a small amount of o-isopropyltoluene (due to steric hindrance effect), it also contains a considerable amount of m-isopropyltoluene. In fact, the ratio of meta-to-para-isopropyltoluene is about 60: 40. The reaction formula as the picture shows.
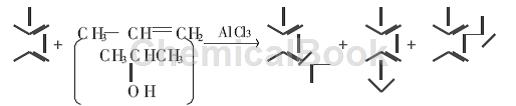
In industry, the mixed product thus obtained is further oxidized and acidolyzed to produce cresol. The cresol produced by this method is also a m- and p-cresol (o-isopropyltoluene is difficult to be oxidized).
2. Synthesis of p-cymene using turpentine as raw material
Synthesis of cumene from toluene has poor selectivity, and highly selective synthesis methods require harsh conditions. Therefore, researchers have been looking for synthetic routes with abundant raw materials and simple methods. The preparation of paracymene from turpentine as raw material has been the focus and hot spot of research in recent years. Turpentine is an abundant renewable resource whose main component is pinene. Using turpentine as theDuring the production process of camphor and terpineol synthesized as raw materials, a large amount of industrial dipentene is produced as a by-product, the main component of which is several monocyclic terpenes with p-diene structures. Pinene and monocyclic terpenes have the same or similar carbon framework structure as p-cymene. Pinene can be isomerized into monocyclic terpenes through hydrogen transfer reaction, and monocyclic terpenes can be converted into monocyclic terpenes through catalytic dehydrogenation. Paracymene. The preparation of paracymene using pinene and monocyclic terpene as starting materials is described below.
1) Using monocyclic terpenes as raw materials
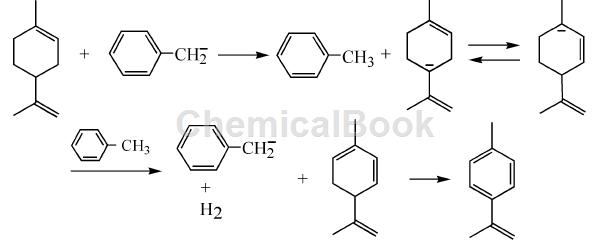
The most studied method is to produce p-cymene through catalytic dehydrogenation using T-limonene as raw material. This was studied as early as the 1920s, and he used a palladium-based catalytic system. Studies have shown that T-limonene disproportionates into p-alkanes and p-cymenes. In the 1950s, metallic sodium was used as a catalyst and benzyl sodium as a cocatalyst to catalyze the dehydrogenation of monocyclic terpenes such as T-limonene to produce p-cymene. Taking T-limonene as an example, the reaction process is shown in the figure.
2) Using bicyclic terpenes as raw materials
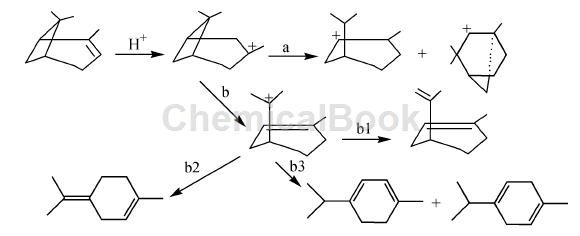
It mainly uses T-pinene as the starting material. T-pinene is first ring-opening and isomerized into monocyclic terpenes, and then undergoes catalytic dehydrogenation to produce p-cymene. The acid-catalyzed ring-opening isomerization reaction of T-pinene was studied. Under acidic conditions, the π bond in the double bond of T-pinene was broken, and a stable tertiary carbocation was first formed. The formed tertiary carbocation was further formed due to tension. For isomeric rearrangement, if an organic acid is used as a catalyst in a low-polarity solvent, process a mainly occurs; if an inorganic acid is used as a catalyst in a polar solvent, process b occurs, as shown in the figure. The subsequent dehydrogenation reaction used copper formate-nickel formate (Cu: Ni= 1: 1) and W-5 type Raney-Ni catalyst.
Main reference materials
[1] Research progress on the synthesis of cumene
[2] CN200710170780.4 A method of synthesizing tona musk
[3] CN201110028569.5 A method for preparing hexamethyltetralin by continuous reaction under ionic liquid catalysis


