[Background and Overview][1][2]
Among a large number of asymmetric synthesis pharmaceutical reagents, the chiral compound α-cyclohexylmandelic acid (Cyclohexylphenylglycolic Acid, referred to as CHPGA) is an important precursor synthesis raw material. Its two optical isomers are (S)-α-cyclohexylmandelic acid and (R)-α-cyclohexylmandelic acid. (S)-α-Cyclohexylmandelic acid is the precursor material for the synthesis of antispasmodic drugs (S)-oxybutynin and (S)-desethylated oxybutynin. S)-Desethyloxybutynin is clinically used to treat urinary urgency, frequent urination and urinary incontinence. Compared with their racemic structures, optically active drugs have more effective pharmacological effects. (R)-α-cyclohexylmandelic acid is prepared from the anticholinergic drug (R)-N-methyl-piperidin-4-yl-2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid methyl iodide salt and (R, R ) – precursor raw material of quinuclidin-3-yl-2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid methyl iodide salt. These two optically active drugs have a strong affinity with muscarine receptors in the body, and their effects are easily absorbed by various tissues in the body. The agglutination rate in plasma in most tissues of the organism is twice that of their racemic configuration. In tests on live mice, they were also metabolized more slowly than the racemates, which enhanced their potency and improved their efficacy. Compared with their racemic structures, optically active drugs have more efficient pharmacological effects. Therefore, the market prospect of single enantiomer α-cyclohexylmandelic acid is very huge. α-Cyclohexylmandelic acid is an important organic synthesis intermediate and is widely used in the synthesis of pesticides and medicines. As its market continues to expand, the demand for α-cyclohexylmandelic acid continues to increase and its application scope gradually broadens.
[Application][2]
Cyclohexylmandelic acid is an important chiral drug precursor, which can be used to synthesize a variety of chiral drugs, such as: Oxybutynin (Ox ybuty nin (OXY for short), Oxphencyclimine, Ox yphenonium bromide, Oxyprronium bromide, Oxyso niumiodide, and its metabolite Desethylo xy butynin, etc. These drugs all have important biological activities and good curative effects. Among them, OX Y is the leading drug for the treatment of urinary incontinence and has a very good market prospect. Pharmacological studies have found that taking racemic OXY can cause side effects such as dry mouth, fatigue, diarrhea, and accelerated heartbeat. This will lead to reduced dosage or intermittent use of the drug, and the use of this drug by the elderly and patients with heart disease is also restricted. Compared with racemic OXY, S-type OXY not only has higher efficacy, but more importantly, has fewer side effects. To prepare (S)-OXY, in addition to the resolution of racemic OXY, it can also be prepared by esterification of its chiral precursor cyclohexylmandelate, and the latter can significantly reduce the cost. Another drug, Oxy pheno nium bromide, also needs to be synthesized from its chiral precursor, cyclohexylmandelic acid.
【Preparation】[1]
There are several preparation methods for racemic cyclohexylmandelic acid.
1. Selective hydrogenation of phenylmandelic acid or phenylmandelic acid ester
Cyclohexylmandelic acid can be produced by hydrogenation of phenylmandelic acid, or by hydrogenation and hydrolysis of phenylmandelic acid ester. Platinum can be used as the catalyst. During the reaction, both benzene rings will be saturated and the by-product dicyclohexyl oxalic acid will be obtained, but cyclohexyl mandelic acid is the main product. This is because phenyl mandelic acid is more easily adsorbed on the catalyst than cyclohexyl mandelic acid. Hydrogenation is carried out, and desorption occurs after hydrogenation. The product can be recrystallized from methanol or ethanol.

2. Grignard reagent method
The equation for preparing racemic cyclohexylmandelic acid by the Grignard reagent method is: In this route, benzoylformate is reacted with cyclohexylmagnesium halide to obtain cyclohexylmandelate, which is then hydrolyzed to obtain cyclohexylmandelic acid. .

3.. By cyclohexene addition method
This method uses methyl benzoylformate (a) as raw material, reacts (a) with cyclohexene in methylene chloride in the presence of titanium tetrachloride to prepare T-(2-cyclohexene After preparing methyl)mandelic acid (b), cyclohexylmandelic acid (d) can be produced by three routes depending on the order of hydrolysis and reduction operations.

Route 1: First reduce (b) to obtain cyclohexylmandelate methyl ester (c), and then hydrolyze to obtain (d), which includes: ① Dissolve (b) in methanol and add 5% mass fraction of Coated with palladium activated carbon; ② Pour hydrogen (350 kPa) into the mixture, stir for 8 h and filter out the catalyst; ③ Add 48.5% NaOH solution with a mass fraction of 48.5% and stir at 75~80°C for 4 h. And evaporate the methanol under reduced pressure; ④ Add toluene, and adjust the aqueous phase to pH=1 with 6 mol/L hydrochloric acid at 60-70°C; ⑤ Cool the organic phase to crystallize and filter to obtain (d). The total yield was 63.1% and the purity was 99.3%.
Route 2: First hydrolyze (b) to obtain α-(2-cyclohexenyl)mandelic acid (e), and then reduce to obtain (d). Except that the operation sequence is opposite to that of route 1, the hydrolysis and reduction are as follows: The purification methods are similar to Route 1. The total yield was 62.2% and the purity was 99.0%.
Route 3: Simultaneously hydrolyze and reduce (b) to prepare (d), that is, dissolve (b) in methanol and add palladium-coated activated carbon and NaO H solution. The other methods are similar.Line 1, the total yield is 55.5%, and the purity is 98.8%.
3. Halogenated cyclohexane alkylation method
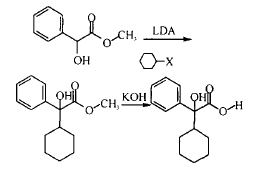
Add n-butyllithium in cyclohexane dropwise at 0°C in the presence of argon gas into a solution consisting of diisopropylamine and dry THF. After 30 minutes, cool the solution to -78°C, and then Add a solution of methyl mandelate and T HF. Stir at -78°C for 15 min and add a solution of alkyl bromide or alkyl iodide in THF. The reaction mixture was stirred at this temperature for 15 min and then at room temperature until the reaction was complete. The resulting reaction mixture was then poured into 1 mol/L HCl, extracted with diethyl ether, washed with 1 mol/L HCl and brine until neutral, dried with Mg SO4, and after removing the solvent, the resulting product was purified on a silica gel column. The route for the alkylation of halocyclohexane is shown in Eq.
[Main reference materials]
[1] Zang Jian. Research progress on asymmetric synthesis of α-cyclohexylmandelic acid[J]. Chemical Intermediates, 2008 (12): 5-9.
[2] Hu Shanshan, Wu Yizu, Shi Meiren. Preparation and separation of α-cyclohexylmandelic acid[J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology, 2004, 13(2): 44-47.
[3] Yuan Han. Preparation method of R-(+)-α-cyclohexylmandelic acid. CN201410063355.5, application date 2014-02-25


