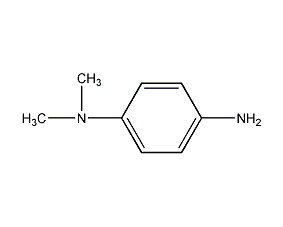
Structural formula
| Business number | 02GX |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H12N2 |
| Molecular weight | 136 |
| label |
4-amino-N,N-dimethylaniline, p-Amino-N,N-dimethylaniline, dimethyl p-phenylenediamine, 4-Animodimethylaniline, 4-Aminodimethylaniline |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-98-9
MDL number:MFCD00007860
EINECS number:202-807-5
RTECS number:ST0874000
BRN number:508105
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless needle-like crystals
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.09
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air =1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 39~40
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 262
6. Boiling point (ºC, 45mmHg): Not determined
7. Refractive index: Not determined
8. Flash point (ºC): 90
9. Specific optical rotation Degree (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC) : Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Can dissolve In alcohol, ether and chloroform.
Toxicological data
Rat abdominal cavity LD50: 21mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 44.80
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 129.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 335.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 17.76
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 29.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 93.4
10. Isotopic atomsQuantity: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond position Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidants, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, and chloroform.
Poisonous. Irritating to skin. Emit toxic gases when exposed to high heat.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. 2. The storage area should be equipped with suitable materials to contain leaks.
Synthesis method
1. Use dimethylaniline as raw material, obtained through nitrosation and reduction. The reaction formula is as follows:
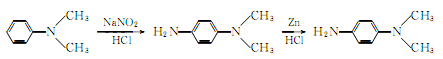
Process: (1) Nitrosification Mix dilute hydrochloric acid and dimethylaniline and cool to below 5℃, add sodium nitrite solution for nitrosation, After addition, place it, filter the crystallization, wash it with 1:1 hydrochloric acid, wash it again with a mixture of hydrochloric acid and alcohol, and drain it to obtain nitrite. (2) Reduction Stir the above crude product with water into a paste, add industrial concentrated hydrochloric acid, cool it with ice water outside, slowly add zinc powder, the adding temperature should not exceed 45°C. (3) Extraction: Add sodium hydroxide solution to alkaline level, then extract with benzene, dry the benzene solution with anhydrous potassium carbonate, recover benzene in a water bath, and then collect the finished product by distillation under reduced pressure. Other preparation methods are obtained by reduction of methyl orange or reduction of p-nitrodimethylaniline with sodium sulfide or potassium sulfide. Industrially, the waste liquid after vanillin extraction is used as raw material, which is obtained through neutralization, extraction and distillation. This product is irritating to the skin and is 8 times more toxic than p-phenylenediamine.
2. The preparation method is to use N, N-dimethylaniline with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid for nitrosation, and then reduce it in the presence of iron powder and hydrochloric acid to obtain N, N-dimethyl The product is obtained by neutralizing p-phenylenediamine hydrochloride with alkali.
The wastewater from coumarin production can also be neutralized with ammonia to pH=7~8, heated to about 40°C, precipitated for 8~12 hours, the precipitated residue is removed, the neutralized liquid is extracted with benzene, and then the pressure is reduced Remove benzene to obtain N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine.
Purpose
Dye intermediates. Used in the production of pesticides and developers. It can also be used to synthesize N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine curing agent and is also a reagent for measuring vanadium.


